Key Facts About Fannie Mae And Freddie Mac
Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac serve similar purposes for American homeowners and the U.S. economy as a whole. These two agencies are important for homeowners as their requirements are often used to set regulations on lending practices. Understanding key points about these agencies can provide insight into the role of Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac:
- Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac were created by the U.S. Congress and are currently in government conservatorship. They provide affordability and stability to the mortgage market.
- The loan guidelines required by Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac can impact your loan terms, including the amount you can borrow, your required down payment, and the credit score you need to qualify for a loan.
- Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac education programs on home buying are designed to help more people become homeowners.
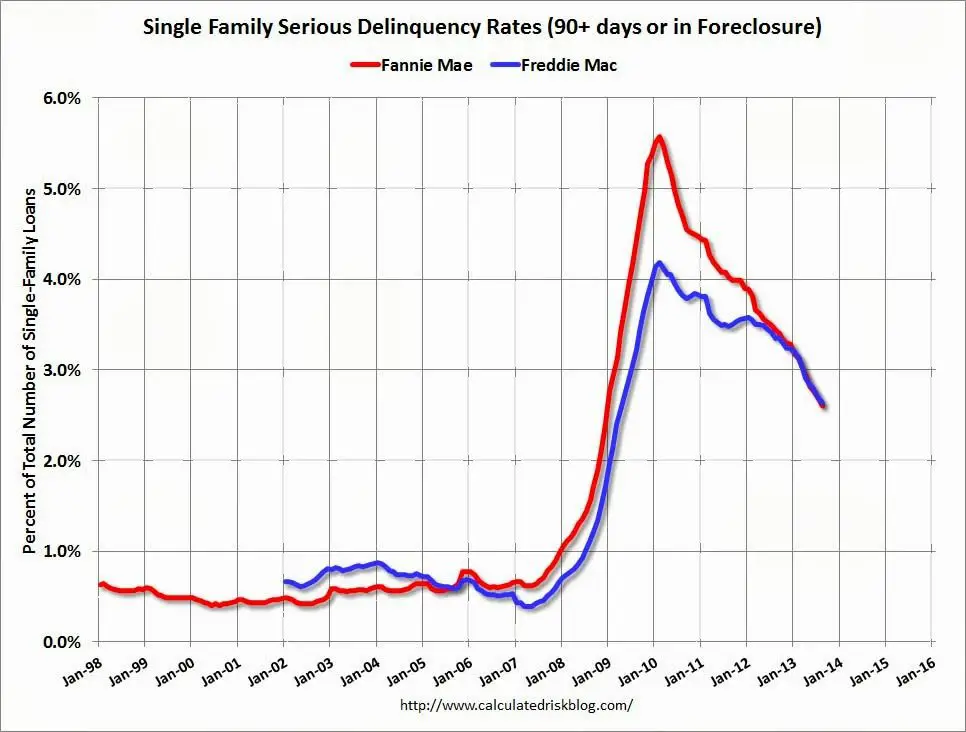
- While Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac struggled to survive during the housing crisis of 2008 and received bailout money, they were able to recover and become profitable once again in 2012. They will likely be released from conservatorship by 2024, if not sooner.
Whether youre shopping for a mortgage or already own a home, you may be directly impacted by Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac. Knowing how these branches work and understanding their similarities and differences can help you make stronger decisions as a homeowner.
About the Author
Fannie Maes Refinow Program
Starting June 5, 2021, Fannie Mae has been offering low-income mortgage holders a new refinance option through a program called RefiNow, meant to reduce their monthly payments and interest rates. To be eligible, homeowners must be earning at or below 80% of their area median income .
This program is intended to help more homeowners refinance by removing some of the barriers of the traditional refinancing process, improving affordability, and promoting sustainable homeownership. Lower-income borrowers typically refinance at a slower pace than higher-income borrowers, potentially missing an opportunity to save on housing costs, says Malloy Evans, senior vice president, and single-family chief credit risk officer, Fannie Mae.
If homeowners are unsure about whether or not Fannie Mae owns their mortgage, they can visit Fannie Maes Loan Lookup Tool. The RefiNow program offers several benefits for homeowners. First, it requires a reduction in the homeowners interest rate by a minimum of 50 basis points and a savings of at least $50 in the homeowners monthly mortgage payment. Second, Fannie Mae will provide a $500 credit to the lender at the time that the loan is purchased if an appraisal was obtained for the transaction, and this credit must be passed on from the lender to the homeowner.
To qualify for RefiNow, a homeowner must meet these qualifications:
More Flexible Lending And Appraisal Standards
The easing of lending and appraisal standards for homebuyers applying for a Fannie Mae- and Freddie Mac-backed mortgage during the pandemic was extended by the FHFA to July 31, 2021, as the final deadline. They allowed:
- Alternative appraisals on purchase and refinance loans
- Alternative methods for documenting income and verifying employment before loan closing
- Expanding the use of powers of attorney to assist with loan closings
Don’t Miss: Rocket Mortgage Qualifications
Which Leads To The Creation Of Freddie Mac
If Fannie Mae was doing so well why did we need Freddie Mac? In fact, there was a worry in Washington that Fannie Mae was doing a little too well.
Freddie Mac was set up in 1970 to create competition. It was designed to give lenders another way to sell their loans. This was meant to push down Fannie Mae fees and charges, and lower mortgage costs overall.
Freddie Mac was set up to create competition with Fannie Mae. They help push down eachothers fees and charges, which keeps mortgage rates low for borrowers.
Like Fannie Mae, Freddie Mac is a GSE. It had the same line of credit with the Treasury, exemptions from state and local taxes, and could ignore securities laws.
So while the two companies look almost identical from the outside, theyre actually in constant competition for mortgage business behind the scenes.
More Eligible Properties Could Help
Access to mortgage funding, even with low down payments, still doesn’t solve the problem of a lack of available housing. Conventional financing is also looking to help address this issue.
Fixer-upper funding wrapped into a home purchase mortgage also with 3% down payments may be one answer. Lawless says Fannie’s renovation loan program has been “clunky” in the past, but has been recently updated and modified to be easier to use.
And Fannie’s MH Advantage program, to finance manufactured housing, also offers 97 LTV financing.
Read Also: 10 Year Treasury Vs Mortgage Rates
Fannie Mae And Freddie Mac Are Government Sponsored Enterprises
Fannie and Freddie are private corporations that were chartered by Congressthe formal term for this kind of company is a Government Sponsored Enterprise . There are several other GSEs, like the Farm Credit System. While GSEs are publicly traded companies, they all serve a very public mission of supporting the nations financial system. Because of the large role they play in the economy and their governmental affiliation, some investors assume they are implicitly guaranteed by the federal government. This means they believe the government would bail out Fannie and Freddie if they couldnt pay back their debts.
Even though Freddie Mac and Fannie Mae are technically shareholder-owned, they have been under government conservatorship since the Great Recession. Many investors who hold stock in the two companies are eagerly waiting for them to emerge from government control so their stock can trade on public exchanges again.
Frequently Asked Questions About Fannie Mae And Freddie Mac
Is Fannie Mae the FHA? No. The Federal Housing Administration is a government agency that insures loans made by lenders to borrowers with low to moderate incomes. FHA loans have more relaxed credit standards than conventional loans purchased by Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac.
What is the difference between a Fannie Mae loan and a conventional loan? They are the same. Conventional loans are the mortgages purchased by the government-sponsored enterprises of Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac.
What are the benefits of a Fannie Mae loan? Fannie and Freddie loans have competitive interest rates and low down payment options. But the biggest benefit of Fannie and Freddie loans: They are the mortgages most lenders prefer to make. There is a ready market where lenders can sell the loans, earn a profit and gain more capital to make additional loans.
Can you get a loan directly from Fannie Mae or Freddie Mac? No, the GSEs only buy qualifying loans from lenders.
How will I know if my loan is sold to Fannie or Freddie? Likely you won’t. The GSEs won’t collect your monthly payment or perform a borrower-facing service. However, they may assist your lender or loan servicer if you are seeking a mortgage loan modification, forbearance plan or disaster relief. You can see if your loan is owned by either firm by using a search tool provided by Fannie Mae or Freddie Mac.
Recommended Reading: Can You Do A Reverse Mortgage On A Mobile Home
Freddie Mac Mortgage Forbearance
If you have a Freddie Mac-owned mortgage, you may be eligible for help if you have been directly or indirectly impacted by the COVID-19 pandemic. There are currently several mortgage relief options if you can’t make your mortgage payment due to a loss or decline in income, including:
- Up to 12 months of mortgage forbearance
- Waived penalties and late fees
- Halt on all evictions until Sept. 30, 2021
- Loan modification options to lower payments or keep payments the same after the forbearance period.
Forbearance is not forgiveness. Ask your mortgage servicer about your post-forbearance options. Be wary if the option is a balloon payment rather than simply adding the unpaid months to the end of your mortgage.
How Fannie Mae And Freddie Mac Work
When the lenders sell the loans, they recoup funds they can use to make more loans. This helps to keep rates low, and it keeps lenders from having to collect penalties from borrowers who refinance their loans or repay them early, to make up for lost interest.
Read Also: Rocket Mortgage Launchpad
What Is The Difference Between Fannie Mae Freddie Mac And Fha
The difference between a FHA and Fannie Mae loans are that the FHA insured loan is a loan by The US Federal Housing Administration mortgage insurance backed mortgage loan that is provided by a approved lender. … The Fannie Mae loan has a higher credit score requirement at 620 to 640 which is higher than the FHA loan.
Fannie Mae And Freddie Mac Similarities
Fannie Mae, Freddie Mac, and the Federal Home Loan Bank system made housing affordable for most Americans for decades. But they functioned as government-sponsored entities. This meant they had to be profitable for the shareholders while creating the secondary market that made the resale of mortgages feasible.
Together, Fannie and Freddie saved the U.S. housing market. By 2009, Fannie Mae, Freddie Mac, and FHLB provided 90% of the financing for new mortgages. That was more than double their share of the mortgage market prior to the 2008 crisis. Private mortgage financing had simply dried up.
After the recession, most banks would not give anyone a loan without Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac guarantees.
Both Fannie and Freddie are now under the conservatorship of the Federal Housing Finance Agency. The U.S. Treasury Department owns all their senior preferred stock. All of their profits go to the U.S. Treasury. Investors can still buy common stock and junior preferred stock. The conservatorship doesn’t allow them to pay dividends.
Recommended Reading: 70000 Mortgage Over 30 Years
Are There Loans That Aren’t Eligible To Be Sold To Fannie Mae Or Freddie Mac
A mortgage loan that is eligible to be acquired by Fannie Mae or Freddie Mac is called a “conforming” loan. It must meet several standards to fall into that category and qualify to be sold to Fannie or Freddie. Loans that don’t meet those standards are nonconforming and can’t be sold. Requirements are based around loan amounts, credit scores, debt ratios, down payments, and property locations or types.
Who Is Eligible For Freddie Mac
Qualifying for HomeOne Freddie Mac 97 percent financingAt least one borrower must be a first-time homebuyer. The property must be a one-unit primary residence including single-family residences, townhomes, and condos. You need at least 3 percent for your down payment. Homebuyer education is required.
Recommended Reading: Who Is Rocket Mortgage Owned By
Fannie Mae And Freddie Mac: Overview
In 1938, the government created Fannie Mae, or the Federal National Mortgage Association, amid the struggles of the Great Depression. The goal of Fannie Mae was to create a more reliable source of funding for homebuyers, opening doors for more Americans, figuratively and literally.
Freddie Mac, short for the Federal Home Loan Mortgage Corporation, came on the scene through an act of Congress in 1970, with a similar purpose. Both Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac now operate under the conservatorship of the Federal Housing Finance Agency .
Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac help facilitate access to long-term, fixed-rate mortgages with installment payments. They do this by buying mortgages from banks and other lenders, giving the lenders more capital to continue creating loans for more borrowers. Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac typically package the loans they buy into mortgage-backed securities in the secondary mortgage market.
Both GSEs played a role in the Great Recession. In the years leading up to the housing market collapse, they backed or owned numerous subprime mortgages. When the housing bubble burst, economic pressures and large losses led to the need for the government to step in with bail-out funding. As a result, Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac were able to help usher the housing market toward recovery.
Similarities: How Fannie Mae And Freddie Mac Help You Save Money
As a mortgage borrower, you cant go to your nearby Fannie Mae or Freddie Bank branch and apply for a loan. Thats because the two companies dont actually sell mortgages.
Instead, what happens is this:
- You get your home loan from a bank or mortgage lender
- The lender sells that mortgage to Fannie Mae or Freddie Mac
- The money Fannie and Freddie pay for mortgages goes back into the pool of local bank and lender funds
- Those lenders use the funds to make more home loans for more borrowers
- More loan money i.e. more supply pushes down lending costs for everyone
Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac get much of their money from investors worldwide by selling interests as mortgage-backed securities . The MBS are created by bundling thousands of mortgage loans together to make a security.
Thanks to the extra revenue Fannie and Freddie bring into the U.S., theres plenty of lending money to go round. That means consumers arent competing for limited funds, and rates stay relatively low.
Also Check: Recast Mortgage Chase
Ginnie Mae: The Lesser
Another layer of protection for investors is offered in the form of the government agency Ginnie Mae . A part of the Department of Housing and Urban Development, Ginnie Mae guarantees the timely payment of mortgage bonds that include federally insured or guaranteed loans, such as FHA mortgages. Fannie and Freddie guarantee loans to secondary market investors, while Ginnie Mae guarantees mortgage bond payments.
For example, if a borrower defaults on their mortgage, Fannie and Freddie are responsible for the losses on the loans they guarantee to investors, while Ginnie Mae is financially responsible for the bond payments to the holders of Ginnie Mae securities.
The relationships may seem complicated, but the ultimate goal of each of these three institutions is clear:
What Fannie Mae Does
As a secondary mortgage market participant, Fannie Mae does not originate mortgage loans. Instead, it keeps funds flowing to lenders by purchasing or guaranteeing mortgages issued by credit unions, banks, thrifts, and other financial institutions. It is one of two large purchasers of mortgages in the secondary market. The other is its sibling Freddie Mac, or the Federal Home Loan Mortgage Corporation, which is also a GSE chartered by Congress.
After purchasing mortgages on the secondary market, Fannie Mae can pool them to form a mortgage-backed security . An MBS is an asset-backed security that is secured by a mortgage or pool of mortgages. Fannie Maes mortgage-backed securities are then purchased by institutions, such as insurance companies, pension funds, and investment banks. It guarantees payments of principal and interest on its MBSs.
Fannie Mae also has its own portfolio, commonly referred to as a retained portfolio, which invests in its own and other institutions mortgage-backed securities. Fannie Mae issues debt, called agency debt, to fund its retained portfolio.
By investing in the mortgage market, Fannie Mae creates liquidity for lenders, which in turn allows them to underwrite or fund additional mortgages. In 2020, Fannie Mae provided $1.4 trillion in liquidity to the mortgage market, which helped low-income Americans buy, refinance, or rent approximately six million homes.
Read Also: Chase Recast
Things You Need To Know About Fannie Mae And Freddie Mac
Fannie and Freddie remain two of the world’s largest financial institutions, but most Americans understand very little about the two mortgage giants.
- John Griffith
Exactly four years ago, during the early days of the financial crisis, the federal government took control of mortgage financiers Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac through a legal process called conservatorship. Since then, the two companies have required roughly $150 billion in taxpayer support to stay solvent, while the government has kept the housing market afloat by backing more than 95 percent of all home loans made in the United States.
Fannie and Freddie remain two of the largest financial institutions in the world, responsible for a combined $5 trillion in mortgage assets. Still, few Americans understand what Fannie and Freddie actually do for homeowners, what part they played in the recent housing crisis, or what role theyll have in the mortgage market of the future. On the fourth anniversary of their conservatorship, here are seven things you need to know about the two mortgage giants.
Did Affordable Housing Goals For Fannie And Freddie Play Any Role In The Subprime Crisis
In 1992 Congress established the affordable housing goals, which were numerical targets for the share of Fannie- and Freddie-backed lending that went to low-income and minority borrowers. For years conservative analysts have falsely pointed to these goals as a catalyst for the housing crisis, claiming they pushed Fannie and Freddie to take on unprecedented levels of risk, creating a bubble and a bust in the subprime housing market that sparked the financial catastrophe.
Thats simply not true. A recent study from the Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis found that the affordable housing goals had no observable impact on the volume, price, or default rates of subprime loans during the crisis, even after controlling for the loan size, loan type, borrower characteristics, and other factors. Federal Reserve Economist Neil Bhutta reached a similar conclusion in 2009, finding that the affordable housing goals had a negligible effect on Fannie and Freddie lending during the housing bubble.
Also Check: Chase Recast Mortgage
Fannie Maes And Freddie Macs Role In Mortgage Markets
Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac purchase mortgages from financial institutions that lend mortgages and then repackage those mortgages into their portfolios or mortgage-backed securities to sell to investors on the secondary mortgage market. By using mortgage-backed securities and guaranteeing on-time principal payments and interest on the mortgages, Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac entice investors to invest in the secondary mortgage market. The attractiveness of the secondary market results in the expansion of housing funds available.