How To Create An Amortization Schedule
An amortization table can provide valuable information for borrowers to consider when taking out a home loan or reviewing their existing mortgage. This useful tool is essential for effective financial planning and greater lifetime savings.
What Is The Best Mortgage Term For You
A mortgage term is the length of time you have to pay off your mortgageâstated another way, itâs the time span over which a mortgage is amortized. The most common mortgage terms are 15 and 30 years, though other terms also exist and may even range up to 40 years. The length of your mortgage terms dictates how much youâll pay each monthâthe longer your term, the lower your monthly payment.
That said, interest rates are usually lower for 15-year mortgages than for 30-year terms, and youâll pay more in interest over the life of a 30-year loan. To determine which mortgage term is right for you, consider how much you can afford to pay each month and how quickly you prefer to have your mortgage paid off.
If you can afford to pay more each month but still donât know which term to choose, itâs also worth considering whether youâd be able to break evenâor, perhaps, saveâon the interest by choosing a lower monthly payment and investing the difference.
What Is Mortgage Amortization
Mortgage amortization is a term that refers to the length of time it would take to pay down the principal balance of a home loan with regular monthly payments. This is based on a period of time known as the amortization period. So a mortgage with a 30-year amortization period would take that long to pay off the principal balance.
Don’t Miss: How Much Is Mortgage Deduction Worth
Two Benefits Of Making Extra Mortgage Payments
As you may know, making extra payments on your mortgage does NOT lower your monthly payment. Additional payments to the principal just help to shorten the length of the loan . Of course, paying additional principal does, in fact, save money since youd effectively shorten the loan term and stop making payments sooner than if you were to make the minimum payment. However, that only happens after a certain period of time.
If you have an extra mortgage payment plan that will end your mortgage within a timeframe that lets you enjoy five years or longer of mortgage-free living, that makes more sense, says Sullivan.
So what is the effect of paying extra principal on a mortgage?
Thoughts On Mortgage Amortization: Learn How Your Mortgage Is Paid Off Over Time
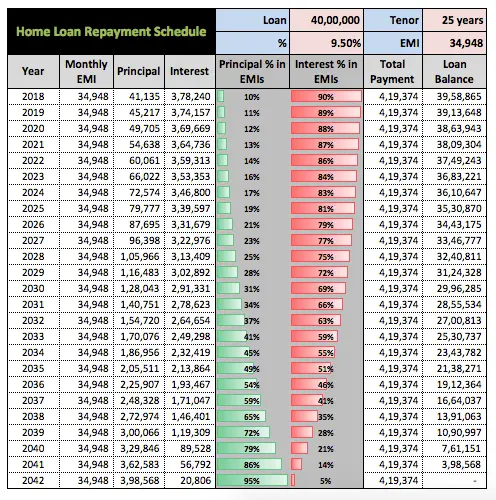
Im 10 yrs into a 30 yrs fixed mortgage at 5.75% with impounds fees included in the mortgage payment of $924.00. I have come to my senses to try and pay down my mortgage at the age of 66 yrs. I still have $108,000 left to pay. I have investigated on getting a refi for a lower rate but if I pay a monthly amount toward the Principal that technically is lowering my APR I have read. My question is this how many years will a $200.00/month to the Principal decrease my 20 years mortgage? Thank you,
Lynda,
Yes, you can reduce your interest expense by paying extra early. To figure out what $200 extra would do per month you can plug in the numbers into an early payoff calculator. It will tell you how much youll save and how quickly the loan will be paid in full. Make sure you specify when those extra payments are actually starting to get accurate figures.
Colin, I am planning to buy a home and say it is worth $35000. If I chose 5 year arm, the monthly mortgage is almost $1500. If I chose 20 year FHA, the monthly mortgage is almost $2000.
If I chose 5 year arm and pay an extra $500 towards principal, does that going to be better than 20 year FHA? At the end of 5 year arm, if I refinance to 15 year fixed.. is that going to make it better?
Thanks,
I have 14 years left on a 30 year loan at 7%, I have finally got my credit score up to where I could refinance. Should I refinance to a 15 or 10 year loan or just keep the loan I have.
Read Also: How Much Is Personal Mortgage Insurance
Payoff In 14 Years And 4 Months
The remaining term of the loan is 24 years and 4 months. By paying extra $500.00 per month, the loan will be paid off in 14 years and 4 months. It is 10 years earlier. This results in savings of $94,554.73 in interest.
If Pay Extra $500.00 per month
| Remaining Term |
| 24 years and 4 months |
| Total Payments |
The Mortgage Payoff Calculator above helps evaluate the different mortgage payoff options, including making one-time or periodic extra payments, biweekly repayments, or paying off the mortgage in full. It calculates the remaining time to pay off, the difference in payoff time, and interest savings for different payoff options.
You May Like: Is The Payoff Amount On A Mortgage Less Than Balance
What Are The Calculation Differences Between Interest And Principal
A mortgage of £200,000 at an interest rate of 3% would attract monthly interest of £500. Should the borrower choose to make an overpayment of £20,000, this would reduce their balance to £180,000. As the balance has reduced, the interest due would also reduce. In this example, on a balance of £180,000, the borrowers monthly interest would reduce to £450 a saving of £50 per month.
Recommended Reading: Is 5.1 Interest Rate Good For Mortgage
Transcript: The Components Of A Mortgage Payment
A mortgage payment is typically made up of four components: principal, interest, taxes and insurance.
The Principal portion is the amount that pays down your outstanding loan amount.
Interest is the cost of borrowing money. The amount of interest you pay is determined by your interest rate and your loan balance.
Taxes are the property assessments collected by your local government. Lenders typically collect a portion of these taxes in every mortgage payment and hold the funds in an account, called an escrow account, until they are due.
Insurance offers financial protection from risk. Like property taxes, homeowners insurance payments are typically held in an escrow account, and then paid on your behalf to the insurance company.
Two main types of insurance can be included as part of your mortgage payment.
Homeowners insurance is required financial protection you must maintain in case your property is damaged by fire, wind, theft, or other hazards. Depending on your geographic location, you may be required to get additional flood insurance.
Mortgage insurance protects your lender in case you fail to repay your mortgage. Whether or not mortgage insurance is required usually depends on the size of your down payment and other circumstances.
In the early stages of your mortgage term, only a small portion of your monthly payment will go toward repaying your original principal.
As you continue to make payments through the years, a greater portion will go to reducing the principal.
Imagine Being Able To Pay Off A Loan Faster Than The Set Term It May Seem Like A Dream But It Can Be Possible If You Can Make And Your Lender Accepts Principal
Principal-only payments are a way to potentially shorten the length of a loan and save on interest. If your lender allows it, you can make additional payments directly toward the amount of money you borrowed the principal which can help you pay off your loan faster.
Lets take a closer look at how you can make principal-only payments, the benefits of doing so and things to consider before you send extra payments to your lender.
Recommended Reading: What Is Included In Mortgage Closing Costs
Structural Mortgage Market Shifts: Increasing Loan Duration & Explicit Government Backing
While the stamp duty holiday was widely discussed, the UK also pushed through other structural shifts to the mortgage market in the wake of the COVID-19 crisis.
“In the UK, usually the longest term fixed mortgage you could normally get was five years. Boris Johnson has now. Nobody can pretend that this has anything to do with Covid, and in fact when Johnson announced it, his stated aim was to give young people access onto the housing ladder. This is a good example of how the magic money tree was discovered for Purpose A, i.e. Covid, and is being used for Purpose B, furthering social justice.” – Russell Napier
When governments guarantee loans they lower the risk of making the loans, which in turn increases the flow of capital into the associated market. That typically leads to faster appreciation.
Programs created to “help” people get into the market are initially effective, but after prices adjust to reflect said capital shifts and risk-free profits the market becomes structurally dependent on such programs & the incremental help they offer declines as prices rise.
The property market has been frenzied throughout the first half of 2021 with Rightmove stating the first half of the year has been the busiest since 2000. Average home prices across England, Wales and Scotland rose to £338,447, an increase of £21,389 or 6.7% since the end of 2020.
Is Making Larger Payments Better For Principal Payments
The larger your principal payment, the more interest youll save. As such, the more you overpay, the greater your savings. The exception to this is where your mortgage has early repayment charges, also known as penalties for overpayments. In this scenario, a penalty may make your overpayment uneconomical if the cost of paying the penalty is higher than the amount of interest saved.
What should you do if you have multiple debts with high interest rates?
Multiple debts refers to when a borrower has borrowed money using a number of separate financial accounts. When faced with a number of debts at higher interest rates, its important that you use your funds wisely to maximise your interest savings. The best way to handle this situation is to pay off the loans with the highest interest rates first. This will allow you to reduce your interest costs faster than any other method.
Once this is done, you should compare products from different lenders to check whether you could reduce your interest costs further by refinancing your loan or mortgage.
You May Like: How Do You Qualify For A Mortgage Modification
Get A Handle On What A Loan Costs You Each Month
If you own a home, you probably know that a portion of what you pay the lender each month goes toward the original loan amount while some gets applied to the interest. But figuring out how banks actually divvy those up can seem confusing.
You may also wonder why your payment stays remarkably consistent, even though your outstanding balance keeps going down. If you understand the basic concept of how lenders calculate your payment, however, the process is simpler than you might think.
Read Also: How Much Is A Mortgage A Month
How Much Of My Mortgage Am I Paying Off Each Month
In the early years of your mortgage, a big chunk of your repayments will simply be paying interest on the capital you’ve borrowed, and a smaller part will pay off your capital.
But the more capital you pay off, the lower your interest repayments will be.
Once you get to the end of your mortgage term, the capital you have borrowed will be repaid – the mortgage will be repaid in its entirety. The table below shows how your interest and capital repayments will change over the term of your mortgage.
In this scenario, you have borrowed £200,000 over a 25-year term, at an interest rate of 5%. Your monthly mortgage repayments are £1,169.18.
| Year |
|---|
Also Check: Can You Get Extra Money On Your Mortgage For Furniture
My Monthly Mortgage Payment Is $500 I Sent A Payment Of $1000 With The Intent Of Applying The Surplus To The Principal But The Bank Applied The Entire Surplus To The Interest Can It Do This
Generally, national banks will allow you to pay additional funds towards the principal balance of your loan. However, you should review your loan agreement or contact your bank to find out their specific process for doing so.
Last Reviewed: April 2021
Please note: The terms “bank” and “banks” used in these answers generally refer to national banks, federal savings associations, and federal branches or agencies of foreign banking organizations that are regulated by the Office of the Comptroller of the Currency . Find out if the OCC regulates your bank. Information provided on HelpWithMyBank.gov should not be construed as legal advice or a legal opinion of the OCC.
Save On Interest With Principal Mortgage Payments
Let’s say you take out a $300,000 30-year fixed rate mortgage with a 5.5% interest rate.
If you pay only your principal and interest every month for 30 years , youâll pay $313,415 in total interest.
But pay $100 extra toward principal every month , and youâll save $46,334 in long-term interest. Plus, youâll pay off your mortgage almost four years sooner. Double that extra payment to $200 dollars , your interest savingsjump to $79,767.
| Monthly PI payment |
| 23 years, 5 months |
| Based on a $300,000 loan for 30-year mortgage with a fixed interest rate of 5.5% |
The more you can pay toward the principal over the life of your loan, the more youâll save in interest â and youâll own your home outright sooner, too!
Don’t Miss: What Is Mortgage Insurance On A Home Loan
How Do You Compare Loan Offers
In any loan scenario, you have to make underlying assumptions such as:
- If you are likely to remortgage the loan again.
- When you are likely to remortgage.
- Where you think interest rates are headed.
- If you think you will sell the home soon.
- If rates head higher and your rate resets well above the initial offer, will your wages be enough to cover payments?
Look Beyond the Monthly Payment
Its important to consider the overall mortgage costs, not just the monthly payment amount. Borrowers will find interest-only payments affordable. However, compared to a full repayment mortgage, you immediately build equity in your home. This bring you closer to home ownership, stability, and grants you further life flexibility. In contrast, interest-only payments do not build equity. It does not provide financial cushion which helps protect you against shifting market conditions.
If one loan amortises and the other does not, then you have to look at how much equity you build in a home. This is a key factor in determining value. Most people also do not want to pay mortgages for the entire lifetime, or until they hit a tough patch and risk foreclosure.
Example Loan Comparison from a Reader
The key to being able to accurately compare mortgage offers is to only adjust a single variable at a time. This way you can easily see the differences between offers, instead of trying to compare apples to oranges.
The example below is based on a question from one of our users named Dan.
| Year |
|---|
How Does Paying Down A Mortgage Work
The amount you borrow with your mortgage is known as the principal. Each month, part of your monthly payment will go toward paying off that principal, or mortgage balance, and part will go toward interest on the loan. Interest is what the lender charges you for lending you money.
Most peoples monthly payments also include additional amounts for taxes and insurance.
The part of your payment that goes to principal reduces the amount you owe on the loan and builds your equity. The part of the payment that goes to interest doesnt reduce your balance or build your equity. So, the equity you build in your home will be much less than the sum of your monthly payments.
With a typical fixed-rate loan, the combined principal and interest payment will not change over the life of your loan, but the amounts that go to principal rather than interest will.
Heres how it works:
In the beginning, you owe more interest, because your loan balance is still high. So most of your monthly payment goes to pay the interest, and a little bit goes to paying off the principal. Over time, as you pay down the principal, you owe less interest each month, because your loan balance is lower. So, more of your monthly payment goes to paying down the principal. Near the end of the loan, you owe much less interest, and most of your payment goes to pay off the last of the principal. This process is known as amortization.
You May Like: How Quickly Can You Get Pre Approved For A Mortgage
When Is An Interest Payment More Advantageous Than A Principal Payment
Paying only interest instead of principal is beneficial if youre looking to keep your monthly payments low to protect your cash flow. Interest payments are almost always required on loans and must be maintained to keep within the lenders mortgage conditions. As such, its important that as a minimum, your mortgage interest is paid on time to avoid formally falling into arrears.
While its important to pay the interest, the principal must also be paid to stay within the good graces of your mortgage lender if your loan was taken on a capital repayment basis. You can learn more about this on our principal payment definition page.
