How Does The Federal Reserve Affect The Housing Market Demand
The Federal Reserve had been boosting the market demand by buying lots of mortgage bonds. Since you dont have to offer as high a rate of return when theres high demand for MBS, mortgage rates were lower than they would be if the Fed wasnt doing all that buying.
The Fed is very interested in MBS buying because, depending on the year, housing makes up 15 18% of overall economic growth.
Of course, theres a flipside to the relationship between bonds and mortgage rates. As the Fed stops buying and even begins to sell some of its holdings, mortgage rates have gone up to entice buyers to get in the market for mortgage bonds.
Secure the best rate with RateShield®.1
Lock and protect your low rate today for 90 days.
Today’s Mortgage Rates For Dec 9 202: Rates Increased
A few important mortgage rates crept higher over the last week. As interest rates rise, it’s getting more expensive to buy a house.
A couple of important mortgage rates are now higher than they were seven days ago. The average 15-year fixed and 30-year fixed mortgage rates both climbed up. The average rate of the most common type of variable-rate mortgage, the 5/1 adjustable-rate mortgage, also advanced.
Mortgage rates have been increasing consistently since the start of 2022, following in the wake of a series of interest rate hikes by the Federal Reserve. Interest rates are dynamic and unpredictable — at least on a daily or weekly basis — and they respond to a wide variety of economic factors. But the Fed’s actions, designed to mitigate the high rate of inflation, are having an unmistakable impact on mortgage rates.
If you’re looking to buy a home, trying to time the market may not play to your favor. If inflation continues to increase and rates continue to climb, it will likely translate to higher interest rates — and steeper monthly mortgage payments. As such, you may have better luck locking in a lower mortgage interest rate sooner rather than later. No matter when you decide to shop for a home, it’s always a good idea to seek out multiple lenders to compare rates and fees to find the best mortgage for your specific situation.
Are Mortgage Rates Pivoting Before The Fed Does
Starting with the Fed’s talking lines on Wednesday, the economic environment, including mortgage rates , shifted last week.
The labor market is still thriving, as seen by another strong employment report released on Friday, which initially drove bond rates higher. However, the way the day concluded indicated that change is on the way.
Read also: Seller’s Market? Buyers Market? Neither, Blame The Lock-In Effect
Investors now have a clearer picture of what the Federal Reserve intends to do with its rate hikes, as well as a lot of evidence indicating that the economy will look different in a year. Investors can also hedge a potential recession by micro-investing in the housing market to earn passive income.
This will be crucial to consider in 2023, especially if the labor market slows down sufficiently to cause a job loss recession, as the Fed desires.
Fed Chairman Powell stated that the Fed does not want to overheat the economy, which would require them to drop rates more quickly later.
It confirms the assumption that much of its aggressive messaging over the last year was targeted at maintaining financial conditions as tight as possible until reaching its neutral fed funds rate.
The Fed did not want mortgage rates to fall or the stock market to rise, but it now looks like a 5% fed funds rate is where they want to go.
Can they make it if they hike at a slower pace? Maybe. One of the two pillars they’re leaning on for their aggressive rate rises in 2022 is the labor market.
Recommended Reading: Can You Roll Student Loan Debt Into A Mortgage
Federal Funds Rate And Helocs
Although there’s merely an indirect link between mortgage rates and the federal funds rate, the Fed does have a direct influence on the rates charged on home equity lines of credit, which typically have adjustable rates.
Interest rates on HELOCs are linked to the Wall Street Journal prime rate, which is the base rate on corporate loans by the largest banks. The prime rate, in turn, moves with the federal funds rate. The prime rate rose to 6.25% after the September 21, 2022, Fed meeting.
On a HELOC with an interest rate of 5%, the monthly interest on a $50,000 balance would be $208.33. A Fed rate increase of 0.75% would raise the HELOC rate to 5.75% and the interest-only monthly payment to $239.58.
How Does Statements From The Fed Affect Mortgage Rates
The work that the Federal Reserve does involves more than only setting the Federal Funds rate. They also hold the responsibility of providing the markets with economic guidance.
If you are one of the rate shoppers, you should be listening to what the Federal Reserve says about inflation. Inflation happens to be the largest threat to mortgage bonds. Mortgage rates typically increase when inflation pressure starts to increase.
There are direct links between inflation rates and mortgage rates. This is exactly what most homeowners experienced in the 1980s.
The inflation was really high and this led to the highest rates for mortgages ever. Both the 30-year and 15-year rates went extremely high and many people will never forget that. The 30-year mortgage rate increased to more than 17%.
The Federal Reserve does not control or set mortgage rates, yet there are direct links between inflation and mortgage rates. Inflation is the term used for describing the loss of purchasing power. When economies experience inflation, consumers are going to need a higher amount of their currency to purchase the same goods.
Inflation is even experienced in grocery stores. A milk gallon that once cost $2 now costs $3. Consumers are forced into spending more money in order to buy the same gallon of milk since the dollar has now lost a portion of its overall value.
When economies experience inflation, the mortgage value will decrease which results in an increase in mortgage rates.
Recommended Reading: How Much Should Your Mortgage Payment Be Compared To Income
What Is The Role Of The Federal Reserve
Established in 1913, the Federal Reserve consists of 12 regional Federal Reserve banks and 24 branches and is run by a board of governors, all of whom are voting members of the FOMC, the Fed’s monetary policymaking body.
The FOMC is responsible for setting overall monetary policy, with the goal of stabilizing the economy and its growth. It does so, in part, by setting the federal funds rate — the benchmark interest rate at which banks borrow and lend their money. When the Federal Reserve raises that rate, banks typically pass on the rate hike to consumers, driving up the overall cost of borrowing in the US. That impacts prospective homebuyers.
“The Federal Reserve is remaining aggressive in raising interest rates to fight inflation and is now, perhaps more significantly, letting their holdings of government and mortgage-backed bonds roll off at twice the pace of the past three months,” says McBride. “Both of these factors are suggestive of further increases in mortgage rates, at least until inflation slows materially,” he adds.
How Raising Interest Rates Helps Fight Inflation And High Prices
The Federal Reserve announced Wednesday another increase in its key interest rate by 0.75% to help fight inflation and get price growth under control.
It’s the fourth time in a row the Fed has raised rates by 0.75%, and the sixth interest rate hike of the year. The Fed hopes that by raising the interest rate, it can slow down the economy and cause prices to come back down.
But how does raising interest rates do that, exactly?
When you get a loan from a bank for example, when you’re buying a house an interest rate is attached to that loan. The interest rate is the price you pay to borrow the money.
Banks need to borrow money, too. Instead of borrowing directly from other banks, they look to the Federal Reserve America’s central bank. Its primary role is to provide a safe and reliable financial system for the U.S. by maintaining deposit accounts for banks.
When banks need to borrow money, they look to other banks that have deposit accounts with the Fed that may be in a surplus.
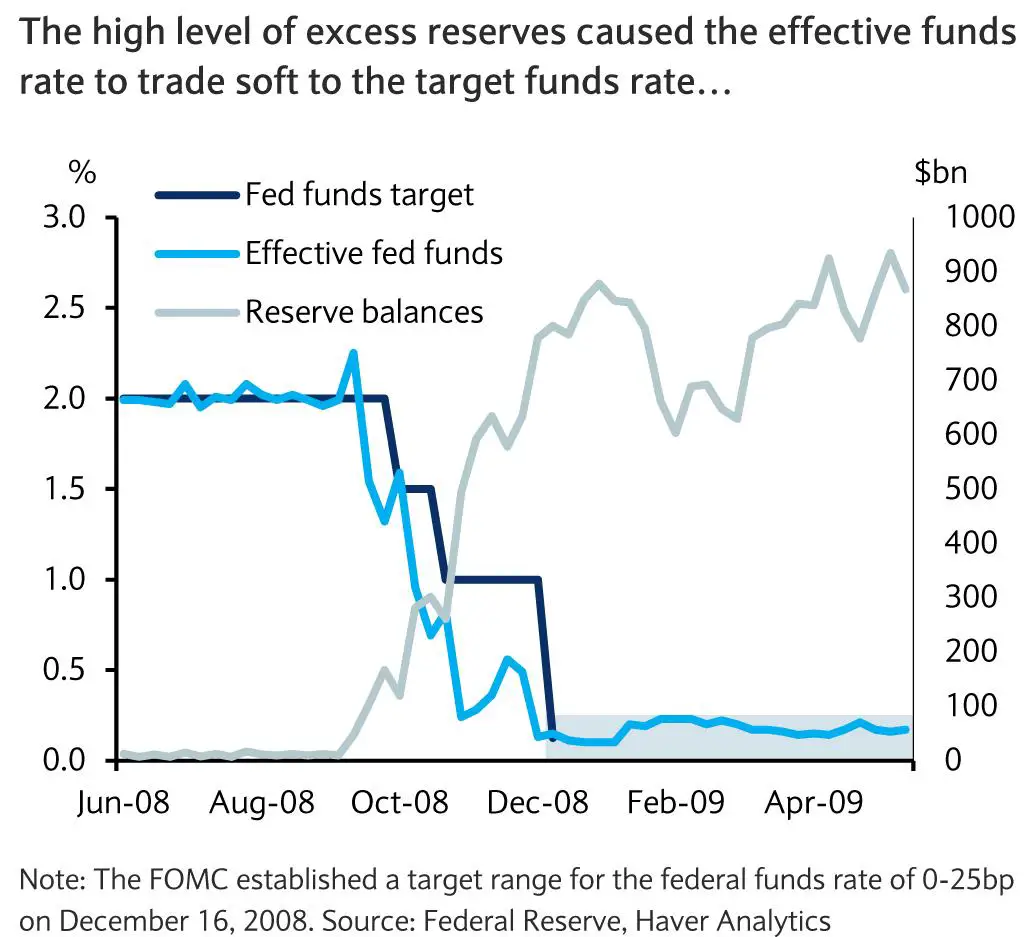
And just as with any other loan, the banks are charged an interest rate for borrowing money. It is this percentage, known as the federal funds rate, that the Federal Reserve helps set with its interest rate announcements.
Recommended Reading: What Is The Mortgage On 800k
Who Controls The Federal Reserve
The Federal Reserve isnt controlled by the government or any of its branches. It is entirely independent and includes 12 Federal Reserve Banks and a Board of Governors. The FOMC includes 7 board members along with a cast of rotating Federal Reserve Bank presidents. The Federal Reserve Open Market Committee is one of the governing bodies of the Federal Reserve. This committee meets every 8 weeks where they review and discuss interest rate policies.
Does The Fed Control Mortgage Rates
Mortgage Q& A: Does the Fed control mortgage rates?
With all the recent hubbub concerning mortgage rates, and the Fed, you might be wondering how it all works.
Does the Federal Reserve decide what the interest rate on your 30-year fixed mortgage is going to be?
Or is it dictated by the open market, similar to other products and services, which are supply/demand driven.
Before getting into the details, we can start by saying the Fed doesnt directly set mortgage rates for consumers. But its a little more complicated than that.
Read Also: How To Qualify For A Second Mortgage
How The Fed Influences Mortgage Rates
The Federal Reserve influences mortgage rates by changing how Wall Street views the future.
The Fed Funds Rate is ill-suited for such a task because its a blunt instrument that changes no more than once every six weeks.
Thankfully, the Fed has a second, more nuanced tool to steer growth in between its meeting its speeches.
On average, at least once per week, a Federal Reserve member appears publicly and speaks about economic growth, threats to the economy, and risks of inflation.
What the Fed says is more important than what the Fed does.
Inflation is when the U.S. dollar is worth less tomorrow than it is today.
Some amount of inflation is healthy and expected. The Fed manages to that. The Federal Reserve has held U.S. inflation near a 2 percent annual target for the last decade. Sometimes, though, inflation advances faster than the Fed wants.
When that happens, everything denominated in U.S. dollars loses value, including mortgage payments.
Mortgages are a 30-year instrument, so inflation hits them hard. Mortgage markets push mortgage rates up because future incoming payments will be less valuable.
Inflation is the enemy of low mortgage rates.
Learn more about mortgages at Mortgage 101.
The Secured Overnight Finance Rate
The Secured Overnight Financing Rate is an interest rate set based on the cost of overnight borrowing for banks. Its often used by lenders to determine a mortgages base interest rate, depending on the type of home loan. Its grown in popularity to serve as the replacement for the London Interbank Offer Rate , which was phased out at the end of 2021.
You May Like: Can I Get A 30 Year Mortgage At Age 55
Fed Rate Hikes In 2022
In March 2022, the Fed raised its federal funds benchmark rate by 25 basis points, to the range of 0.25% to 0.50%. The rate hike marked the first time since 2018 that the Fed has increased rates.
In early May 2022, the Federal Reserve issued another statement that it would again raise the target range for the federal funds rate to between 0.75% and 1%. In an effort to lessen the size of the Federal Reserves balance sheet, the Fed also announced that it would be reducing its holdings of Treasury and mortgage-backed securities.
In June 2022, the Fed raised the rate by an additional 75 basis points, or 0.75%, in an effort to curb the continued elevation of inflation. This increase brought the target rate range between 1.5% and 1.75%, and it marked the largest single rate hike since 1994.
In July, after Consumer Price Index numbers showed inflation was 9.1% on an annual basis, the Fed raised interest rates an additional 0.75% to a target range of 2.25% 2.5%. The hope is that this takes a bite out of inflation, but it also will likely push interest rates higher for borrowers.
The Fed anticipates additional rate hikes will be necessary to hit their target inflation rate of 2%. In fact, many experts predict increases throughout 2022 with the next anticipated hike happening in September. The remaining meetings on the Fed calendar are in September, November and December.
Is It Possible To Estimate Your Interest Rate
Current interest rate information is widely available online. Often you can visit a lenders website directlysuch as Bank of America or Discover Home Loansto find out what their current mortgage interest rates are, which can help you estimate what you might be offered.
There are also mortgage payment calculatorsalso available online that include interest rates in their calculations once you provide a bit of basic information, such as down payment and home price. As you embark upon home shopping, its a good idea to do your research and find out what your interest rate and mortgage payment might be.
You might even consider getting pre-approved for a mortgage with various lenders, to find out what rates you might be offered.
Recommended Reading: What Is The 30 Year Mortgage Rate Now
Do Mortgage Rates Follow Fed Rates
The Fed and the mortgage market move like dance partners: Sometimes the Fed leads, sometimes the mortgage market leads, and sometimes they dance on their own.
The federal funds rate and mortgage rates usually move in the same direction. But it’s sometimes hard to say whether mortgage rates follow the Fed’s actions or the other way around.
The FOMC prefers to give investors a heads-up whenever it plans to raise or cut short-term interest rates. Members of the committee advertise their intentions by sprinkling hints into their public speeches. By the time the committee meets, there’s usually a consensus among investors as to whether the Fed will cut rates, raise them or keep them unchanged.
As that consensus solidifies before an FOMC meeting, mortgage rates usually drift in the direction that the Fed is expected to move. Often, by the time of the meeting, mortgage rates already reflect the expected rate change.
At the same time, mortgage rates move up and down daily in reaction to the ebb and flow of the U.S. and global economies, which are the same developments that the Fed responds to. Occasionally, the Fed and mortgage rates move in opposite directions.
» MORE: Compare current mortgage interest rates
Does The Government Control Mortgage Rates
Thinking the Federal Reserve will cut interest rates, or raise interest rates, may not be advisable. Here are some pertinent comments from an economist:
If the Fed makes dramatic cuts in short-term interest rates to try to stimulate economic growth, that may help stock market investors in the short run. But such a move could also send mortgage rates up, because it will get bond market investors worried about inflation.
The Fed does not control mortgage rates, they control the Fed Funds Rate and the Discount Rate, which are more short term rates. These short term lending rates do not have much effect on long term rates, like mortgage rates for example. The media really does a poor job explaining this when they report that the Federal Reserve lowered interest rates 0.50% today! Then I get dozens of phone calls expecting the 5.00% mortgage rate I was quoting the previous day to suddenly be 4.50%.
What controls mortgage rates is the marketplace, and the market watches inflation like a hawk. Keep this in mind as we all watch mortgage rates.
If there is an inflationary event, like binge borrowing by our government, or a spike in employment, or an increase in CPI numbers, they would all have more affect on mortgage interest rates than anything the Federal Reserve does.
Also Check: What Is The Minimum Down Payment Required For A Mortgage
What Influences Mortgage Rates
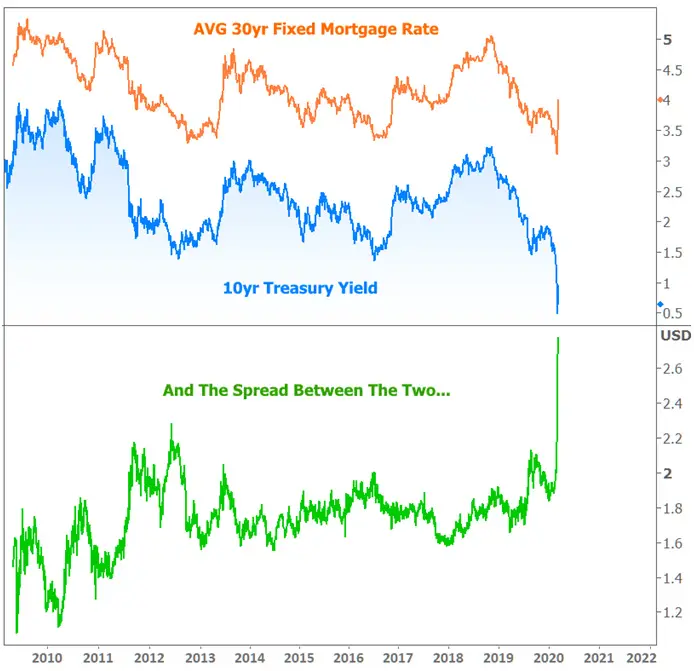
Fixed-rate mortgages are tied to the 10-year Treasury rate. When that rate goes up, the popular 30-year fixed-rate mortgage tends to do the same, and vice versa.
Rates for fixed mortgages are also influenced by other factors, such as supply and demand. When mortgage lenders have too much business, they raise rates to decrease demand. When business is light, they tend to cut rates to attract more customers.
Price inflation pushes on rates as well. When inflation is low, rates trend lower. When inflation picks up, so do fixed mortgage rates.
The secondary market where investors buy MBS plays a role, too. Most lenders bundle the mortgages they underwrite and sell them in the secondary marketplace to investors. When investor demand is high, mortgage rates trend a little lower. When investors arent buying, rates may rise to attract buyers.
The Feds actions do indirectly influence the rates consumers pay on their fixed-rate home loans when they refinance or take out a new mortgage.
What Other Factors Influence Mortgage Rates
As you can see, the Fed only plays an indirect role in setting your mortgage rate.
Lets take a look at some of the other factors that influence mortgage rates. This will help you figure out what you can work on as a borrower to get a great mortgage rate, and what things are simply out of your control.
Recommended Reading: How Many Mortgage Points Can I Buy
