How A Hybrid Adjustable
The 5/1 hybrid ARM may be the most popular type of adjustable-rate mortgage, but its not the only option. There are 3/1, 7/1, and 10/1 ARMs as well. These loans offer an introductory fixed rate for three, seven, or 10 years, respectively, after which they adjust annually.
Also known as a five-year fixed-period ARM or a five-year ARM, this mortgage features an interest rate that adjusts according to an index plus a margin. Hybrid ARMs are very popular with consumers, as they may feature an initial interest rate significantly lower than a traditional fixed-rate mortgage. Most lenders offer at least one version of such hybrid ARMs of these loans, the 5/1 hybrid ARM is especially popular.
Other ARM structures exist, such as the 5/5 and 5/6 ARMs, which also feature a five-year introductory period followed by a rate adjustment every five years or every six months, respectively. Notably, 15/15 ARMs adjust once after 15 years and then remain fixed for the remainder of the loan. Less common are 2/28 and 3/27 ARMs. With the former, the fixed interest rate applies for only the first two years, followed by 28 years of adjustable rates with the latter, the fixed rate is for three years, with adjustments in each of the following 27 years. Some of these loans adjust every six months rather than annually.
Hybrid ARMs have a fixed interest rate for a set period of years, followed by an extended period during which rates are adjustable.
/1 Arm Versus 5/5 Arm Example
A Financial Samurai reader commented,
I closed on a purchase in February with a 5/5 ARM at 1.875%. The margin is 2% and the adjustment cap is 2%. The index is the 5-year Treasury yield. The lifetime maximum rate is 6.875%.
Therefore, the maximum interest rate from years 6-10 would be 3.875%. The other ARM I considered was a 5/1 with 2.5% margin and a lifetime maximum rate of 7.875%. The index would have been the one-year Treasury. Adjustment cap is also 2%.
Id like to think I made the better choice with the 5/5 vs. the 5/1. Maybe when the rate resets, the difference between the 5-year and 1-year yield would be less than 0.5%? What do you think?
. That may have been a bank error in my favor!)
I think the reader made a great choice in taking out a 5/5 ARM instead of a 5/1 ARM.
First of all, paying a lower margin is better. The margin is the profit the bank makes off you. Second of all, currently, rates are going up more on the short end compared to the long end. The 5/5 ARMs index is off the 5-year Treasury yield whereas the 5/1 ARMs index is based on the one-year Treasury yield.
Finally, the certainty of having to pay a maximum of 3.875% from years 6-10 is comforting. Even if the 5/5 ARM adjusts by the maximum 2%, the combined 10-year mortgage rate average is only 2.875%.
The Difference Between A 5/1 Arm And 5/5 Arm And When To Get Either
Updated: by Financial Samurai
Have you ever wondered what the difference is between a 5/1 ARM and a 5/5 ARM or a 7/1 ARM and a 7/6 ARM and so forth? Let me explain in this article because the difference adds to another dilemma mortgage borrowers should consider.
An adjustable-rate mortgage is a home loan with an introductory fixed interest rate upfront, followed by a rate adjustment after that initial period. The introductory fixed interest rate period is signified by the first digit, i.e. 5-year fixed-rate period for a 5/1 ARM.
The fixed-rate period after the initial introductory period is over is signified by the second digit, i.e. 1-year fixed-rate period for the new rate for a 5/1 ARM.
The primary difference between a 5/1 and 5/5 ARM is that the 5/1 ARM adjusts every year after the five-year lock period is over. Whereas a 5/5 ARM adjusts every five years.
Given we know ARMs make up only a tiny portion of total loans, ARMs with an adjustment fixed-rate period of more than one year are even more rare. But lets discuss anyway.
You May Like: Which Lender Has The Best Mortgage Rates
What Is The Difference Between A 5/1 Arm Refinance Loan And A 15
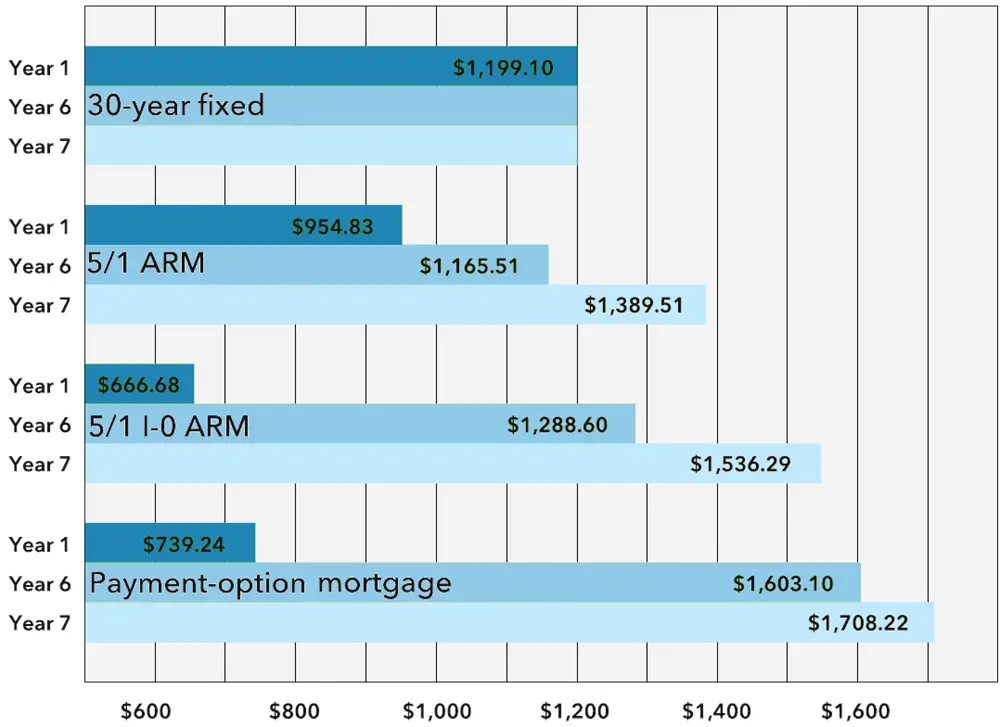
The 5/1 ARM has a fixed rate for five years and an adjustable rate for the remaining life of the loan. Your monthly payment could increase substantially after the first five years if the index rate increases. By contrast, a 30-year fixed-rate refinance loan has a fixed rate and fixed monthly payment for the entire 30-year term. A 15-year fixed-rate refinance loan has a fixed rate and fixed monthly payment for the entire 15-year term.
Learn more about the differences between a 5/1 ARM and a 15- or 30-year fixed-rate loan.
Make An Informed Decision
Buying a home will probably be the biggest financial decision of your life. Make sure you understand your reference rate, margin & how your monthly loan payments might change in the worst case scenario before signing an ARM loan contract.
The CFPB Consumer handbook on adjustable-rate mortgages, which offers consumers an introductory guide to ARM loans including a mortgage shopping worksheet. We’ve included an HTML version of their mortgage shopping worksheet below. You can also download this worksheet & bring it to your financial institution. We offer versions in the following formats: PDF, Word& Excel.
| Basic Loan Information | |
|---|---|
For any home loan you are interested in the lender should be able to give you the above information before requiring you to pay any nonrefundable fees. If you remain uncertain after speaking with your lender, please consider contacting a local housing counselor or call the U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development toll-free at 800-569-4287.
If you found this guide helpful you may want to consider reading our comprehensive guide to adjustable-rate mortgages.
You May Like: What Is Coe In Mortgage
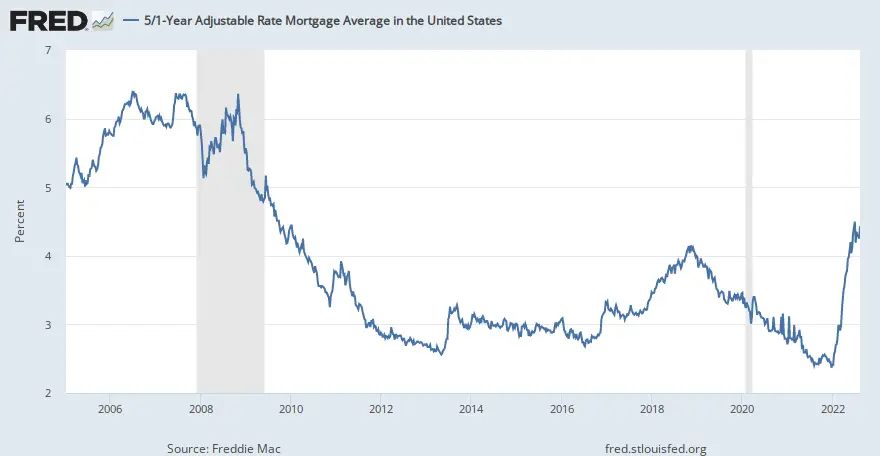
How Do Historical Mortgage Rates Compare
When obtaining an ARM make sure to ask what the Annual Percentage Rate is on the loan. If the initial rate is lower than that rate one might expect payments to increase significantly even if the reference rate the loan is indexed against does not change.
Currently the spread between FRMs & ARMs is quite low, which makes fixed-rates a relatively better deal. As interest rates rise, typically the spread between fixed & adjustable loans increases significantly, which can make ARM loans a more attractive option.
Here are historical average annual interest rates for popular home loan products.
| Year |
|---|
| $187,858.84 |
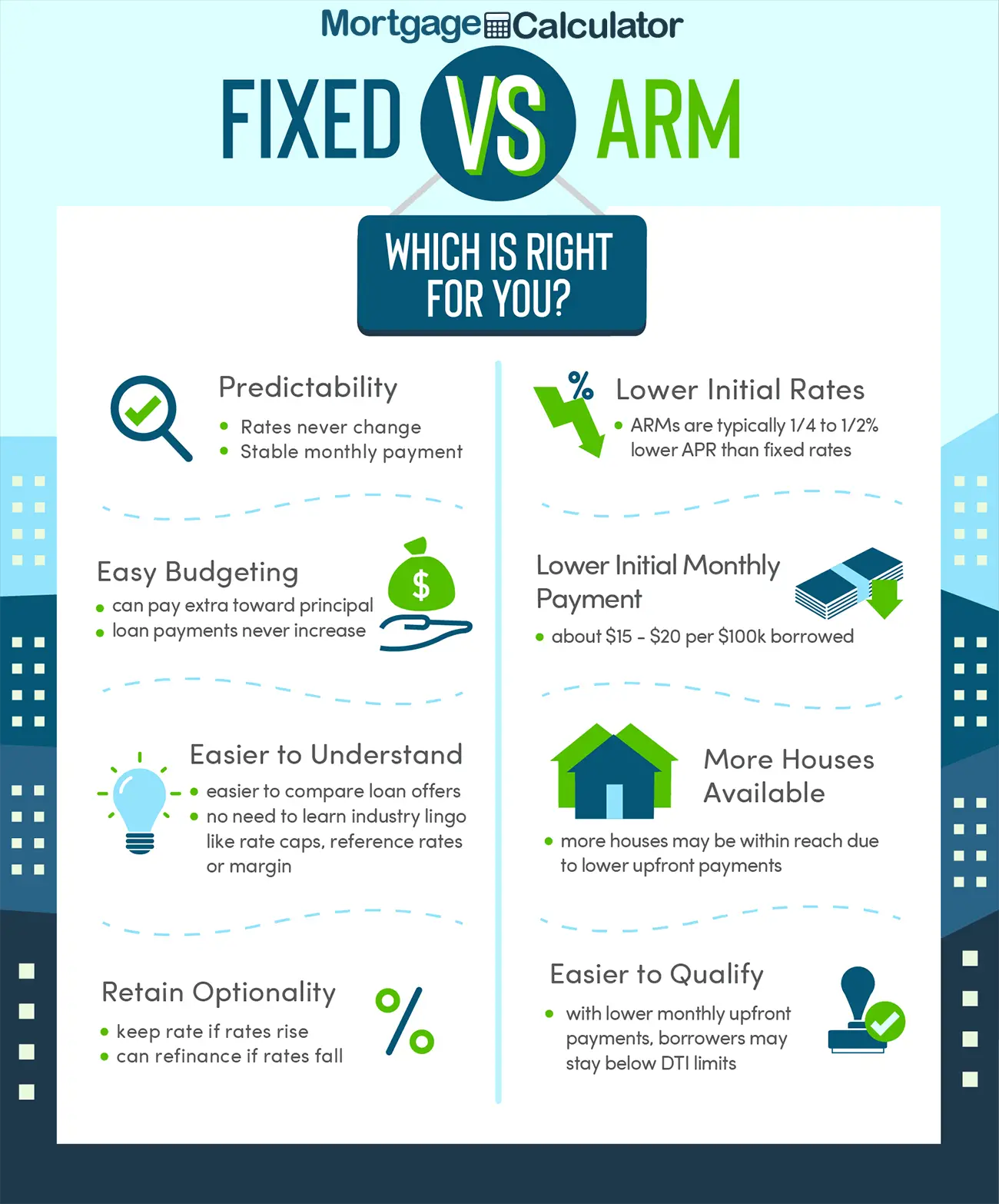
Pros And Cons Of A 5/1 Arm
Is a 5/1 ARM a good idea? ARM rates may be easier on your wallet at first, but there are longer-term risks. Understanding the advantages and disadvantages of a 5/1 ARM will help you make the most informed decision.
| Pros | |
|---|---|
| Your interest rate is lower for the first five years | Your interest rate is likely to rise after the first five years |
| Your monthly payment is lower for the first five years | Your payments might become unaffordable after the rate adjusts |
| You can use the extra monthly savings to pay your mortgage off faster | Your homes value could drop, leaving you stuck in an ARM longer than you planned |
| You could opt for interest-only payments to save extra money each month | Youll make less when you sell your home if you choose an interest-only option |
Also Check: Can You Get A Mortgage While In Chapter 13
/1 Arm Loan: Everything You Need To Know
If youre looking to buy a home, you might be overwhelmed with the sheer number of mortgage choices. Mortgage lenders offer a variety of options when it comes to the type of financing you can get to buy or refinance a home. In addition to varying loan types and terms, youll have to decide whether you want a fixed-rate loan or an adjustable rate mortgage loan .
In this article, well be discussing the 5/1 ARM, which is an adjustable rate mortgage with a rate thats initially fixed at a rate lower than comparable fixed-rate mortgages for the first 5 years of your loan term.
What Is A 5/1 Mortgage Loan
A 5/1 mortgage loan provides the assurance that your interest rate won’t change for the first 60 months of your loan. This can be a very good thing if you lock in a low interest rate just before rates go up. Beginning in the sixth year, however, the rate will adjust annually.
How much the rate will adjust depends on the mortgage index to which the loan is tied. It might rise, or it might go down. Mortgage rate indexes can fluctuate often depending on the economy, market conditions, and other factors. Theres no way to predict how a 5/1 loans rate will change, or by how much, so there’s some level of uncertainty after that five-year period expires.
Read Also: How To Calculate An Adjustable Rate Mortgage
When To Consider A 5/1 Arm
Opting for a 5/1 ARM makes sense if you dont plan on living in your home for the long-term. If you intend to sell the home within five years, you can take advantage of the ARMs lower initial fixed interest rate and lower initial monthly payment.
If youll be in the home for five years or more, an ARM is riskier. Since the rate can fluctuate, you might end up with a higher interest rate and minimum monthly payment.
If you decide to refinance before the end of the fixed term, realize that you might have to pay refinancing closing costs that could negate the savings from the lower interest and payments.
Miranda Marquit is a mortgage, investing, and business authority. Her work has appeared on NPR, Marketwatch, FOX Business, The Hill, U.S. News & World Report, Forbes, and more.
Does Refinancing Hurt Your Credit
Refinancing will hurt your credit score a bit initially, but might actually help in the long run. Refinancing can significantly lower your debt amount and/or your monthly payment, and lenders like to see both of those. Your score will typically dip a few points, but it can bounce back within a few months.
You May Like: Are Home Mortgage Rates Going Down
Potential For A Higher Mortgage Payment Long
The teaser rate on ARMs is lower than the prevailing market rate on fixed-rate mortgages because investors know the interest rate can adjust over time if rates increase. As such there is the potential for your long-term payment to be higher, potentially increasing to the lifetime cap depending on market conditions.
To combat this, you can refinance into a fixed-rate loan if you qualify.
It Will Not Work Well With Long
For those who intend to hold on to a property for more than five years, an ARM loan might not be suitable for them. While the initial fixed interest rate is lower, the succeeding yearsâ rates could spike significantly depending on the real estate market and other economic factors. This means that a property owner will most likely pay more interest over time.
Recommended Reading: How Much Is Monthly Payment On 600 000 Mortgage
/1 Arm Vs 7/1 Arm: Whats The Difference
A 7/1 ARM loan functions in the same way as a 5/1 ARM loan. Both loan options begin with a fixed-rate mortgage that then becomes variable after a number of years. The origination process is also the same for both loan types, but there are two key differences.
- 1.Fixed-rate term: A 5/1 ARM keeps a fixed rate for five years before shifting to an adjustable-rate mortgage . With a 7/1 ARM, the fixed-rate loan expires after seven years.
- 2.Rate savings: A 5/1 ARM offers a lower initial mortgage rate than a 7/1 ARM. While borrowers enjoy two extra discounted years under a 7/1 ARM, such savings will be more modest from year to year compared to a 5/1 ARM.
What Should I Look For When Shopping For A 5/1 Arm
When youre comparing loan options, there are some special numbers to pay attention to when looking specifically at ARMs. For example, you may see one advertised as a 5/1 ARM with 2/2/5 caps. Lets break down what that means, one number at a time.
- Fixed or teaser rate period: The first number specifies how long the rate stays fixed at the beginning of the term in this case, 5 years.
- Adjustment intervals: The next number tells you how often the rate adjusts once the fixed-rate portion of the loan is over. For this example, the 5/1 ARM adjusts once per year.
- Initial cap: The first cap is a limit on the amount the rate can adjust upward the first time the payment adjusts. In this case, regardless of market conditions, the first adjustment cant be an increase of higher than 2%.
- Caps on subsequent adjustments: In our example above, with each adjustment after the first one, the rate cant go up more than 2%.
- Lifetime cap: The final number is the lifetime limit on increases. Regardless of market conditions, this mortgage interest rate cant go up more than 5% for as long as you have the loan.
Other than the margin in your loan documentation, theres no limiting factor to how much your interest rate could adjust down in any particular year if interest rates have moved lower.
Find out if an ARM is right for you.
See rates, requirements and benefits.
Also Check: What Is A Future Advance Mortgage
What Is A 5/1 Arm Interest
An interest-only loan is a type of non-conforming mortgage that charges only interest for a set introductory period. For example, if you choose a 5/1 interest-only ARM, youll only make interest payments for the first 5 years. Thereafter, your mortgage would start amortizing, which means you would begin paying principal and interest as part of your monthly mortgage payment. We dont offer these types of loans.
Is A 5/1 Arm A Good Deal
ARMs aren’t as beneficial as fixed-rate mortgages right now.
There used to be some major advantages to ARMs. Lenders would offer a lower interest rate during the intro rate period than they would offer for fixed-rate mortgages. The low intro rate made an ARM a good deal if you planned to move before the intro rate period ended, because you’d pay a lower rate and never risk an increase.
But these days, fixed rates are comparable to or lower than ARM intro rates, so you’d no longer benefit from a better intro rate.
Mortgage rates are also at historic lows overall, so it could be a better idea to lock in a super low rate with a fixed-rate mortgage than to risk an increase later with an ARM. Rates won’t stay this low forever, so it’s probable your ARM rate would go up at some point before you paid off your mortgage.
Still, each lender works differently. If you’re interested in an ARM, talk to a lender about your options.
Recommended Reading: How Many Months Bank Statements For Mortgage
The Most Common Arm Fixed
An ARM generally has a lower mortgage rate than a 30-year fixed-rate mortgage because it is on the shorter end of the yield curve. As a result, more people will likely take out ARMs as mortgage rates go higher.
In a 3/1 ARM, the initial fixed interest rate period is three years. In the more common 5/1 ARM, the initial fixed interest rate period is five years. Personally, I have a 7/1 ARM with an initial fixed-rate period of seven years.
Then there is the 10/1 ARM with an initial fixed-rate period of ten years. 10/1 ARMs are not as common because they start encroaching on the 15-year fixed-rate mortgage, which tends to have very competitive rates.
Please note there are also 7/6 ARMs and 10/6 ARMs! The 6 represents six months, not six years. In other words, after the introductory rate period is over, the new mortgage interest rate will adjust every six months.
How To Find Personalized 5/1 Arm Rates
We’re showing today’s average mortgage rates, but you can find personalized rates based on your down payment amount, credit score, and debt-to-income ratio.
If you’re a little further along in the homebuying process, then you can speak with multiple lenders to receive personalized rates to compare and contrast rates before choosing a lender.
Also Check: How To Pay Off 100 000 Mortgage In 5 Years
How Does Policygenius Make Money
Were an independent insurance broker, so we get paid a commission by insurance companies for each sale. Insurance commissions are already built into the price of an insurance policy, so youre not paying any extra for working with us to buy a policy. Our compensation on any particular purchase may vary depending on a number of factors, including the type and size of product, the insurer, and the volume of business we have with an insurer, but we don’t push for or give preference to any one insurer over another because of the commission. We’re here to fight for you, not for ourselves.
Disadvantages Of A 5/1 Arm
While a 5/1 ARM can fit some home buyers’ needs, such mortgages are not for everyone. A few key drawbacks include:
Don’t Miss: How To Qualify For Mortgage Modification
