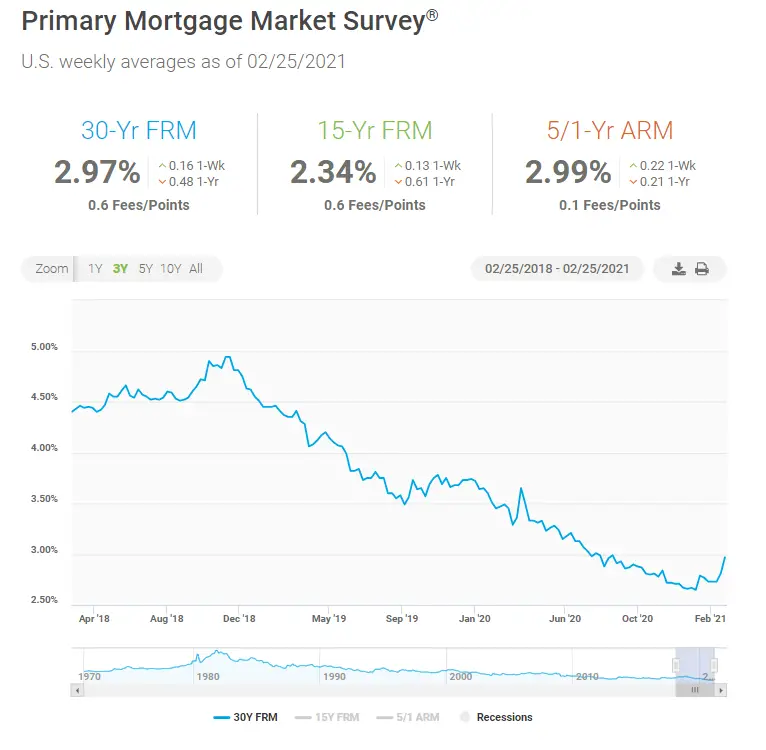
Us Mortgage Rates Hit The Highest Level Since May 2020
Mortgage rates were on the rise once more in the first week of 2022.
In the week ending 6th January, 30-year fixed rates increased by 11 basis points to 3.22%. 30-year fixed rates had risen by 6 basis points in the week prior. As a result, 30-year fixed rates held above the 3% mark for an 8th consecutive week.
Compared to this time last year, 30-year fixed rates were up by 55 basis points.
30-year fixed rates were still down by 172 basis points, however, since November 2018s last peak of 4.94%.
What Does The Future Hold For The Average Mortgage Interest Rate
With the base rate being at an all-time low, the only way is up. The question is, when? We have already seen a resurgence of the property market since the first lockdown in early 2020 and we predict further improvements as restrictions ease and we tip toe back towards normal life, but will rates follow a similar pattern?
A Reuters poll revealed that these rates are expected to remain at 0.1% until at least 2024 to avoid negative borrowing costs.
Mortgage Bankers Association Rates
For the week ending 31st December, the rates were:
-
Average interest rates for 30-year fixed with conforming loan balances rose from 3.31% to 3.33%. Points increased from 0.38 to 0.48 for 80% LTV loans.
-
Average 30-year fixed mortgage rates backed by FHA increased from 3.39% to 3.40%. Points increased from 0.37 to 0.42 for 80% LTV loans.
-
Average 30-year rates for jumbo loan balances decreased from 3.35% to 3.31%. Points rose from 0.34 to 0.38 for 80% LTV loans.
Weekly figures released by the Mortgage Bankers Association showed that the Market Composite Index, which is a measure of mortgage loan application volume, declined by 2.7% from 2-weeks earlier. The Index had slipped by 0.6% in the week ending 17th December.
The Refinance Index declined by 2% from 2-weeks ago and was 40% lower than the same week one year ago. The index had risen by 2% in the week ending 17th December.
In the week ending 31st December, the refinance share of mortgage activity rose from 63.9% to 65.4%. The share had increased from 63.3% to 65.2% in the week ending 17th December.
According to the MBA,
Also Check: How To Get Mortgage Forgiveness
Mortgage Lenders That Help You Score A Lower Rate
Much of your mortgage rate will depend on personal factors such as where you live, your credit score and how much you expect to put as a down payment, plus the mortgage type, term and amount. That said, some mortgage lenders are known for helping homebuyers get as low a rate as possible.
For example, SoFi offers a 0.25% discount when you lock in a 30-year rate for a conventional loan, while another special gives customers up to $9,500 in cash back when they purchase a home through the SoFi Real Estate Center, which is powered by HomeStory. SoFi members can also get $500 off on their mortgage loans.
-
Apply online for personalized rates fixed-rate and adjustable-rate mortgages included
-
Types of loans
Conventional loans, jumbo loans, HELOCs
How Do Mortgage Rates Work
The mortgage rate a lender offers you is determined by a mix of factors that are specific to you and larger forces that are beyond your control.
Lenders will have a base rate that takes the big stuff into account and gives them some profit. They adjust that base rate up or down for individual borrowers depending on perceived risk. If you seem like a safe bet to a lender, you’re more likely to be offered a lower interest rate.
Factors you can change:
-
Your . Mortgage lenders use credit scores to evaluate risk. Higher scores are seen as safer. In other words, the lender is more confident that you’ll successfully make your mortgage payments.
-
Your down payment. Paying a larger percentage of the home’s price upfront reduces the amount you’re borrowing and makes you seem less risky to lenders. You can calculate your loan-to-value ratio to check this out. A LTV of 80% or more is considered high.
-
Your loan type. The kind of loan you’re applying for can influence the mortgage rate you’re offered. For example, jumbo loans tend to have higher interest rates.
-
How you’re using the home. Mortgages for primary residences a place you’re actually going to live generally get lower interest rates than home loans for vacation properties, second homes or investment properties.
Forces you can’t control:
» MORE: What determines mortgage rates?
Don’t Miss: Can I Have A Co Signer On A Mortgage
Mortgage Rates In The 1980s
The 1980s was the most expensive decade for mortgage borrowing largely due to consistently high inflation. By late 1981, mortgage rates averaged more than 18%, an astronomical price compared to todayâs standards.
Paul Volcker, the chairman of the Federal Reserve Board from 1979 to 1987, had the uphill task of rescuing the economy from âstagflation,â a term used to describe stagnant growth and high inflation.
Volckerâs monetary policy of focusing on bank reserves and limiting the money supply pushed the country toward a recession that lasted from 1980 until 1983. Inflation fell to 3.2% in 1983, from an all-time high of 13.5% in 1980, and the economy rebounded. Mortgage rates began falling in 1982, ultimately dropping to 9.78% by the end of the decade.
Variable Interest Rate Mortgage
A variable interest rate can increase and decrease during your term. If you choose a variable interest rate, your rate may be lower than if you selected a fixed rate.
The rise and fall of interest rates are difficult to predict. Consider how much of an increase in mortgage payments youd be able to afford if interest rates rise. Note that between 2005 and 2015, interest rates varied from 0.5% to 4.75%.
Consider if youre comfortable with the possibility of interest rates increasing. Determine if your budget could handle higher payments. If not, a fixed interest rate mortgage may be better for you. You may also consider fixed payments with a variable interest rate.
A variable interest rate mortgage may be better for you if youre comfortable with:
- your interest rate changing
- your mortgage payments potentially changing
- the need to follow interest rates closely if your mortgage has a convertibility option
Get information on current interest rates from the Bank of Canada or your lenders website.
Also Check: Can I Refinance My House With A Second Mortgage
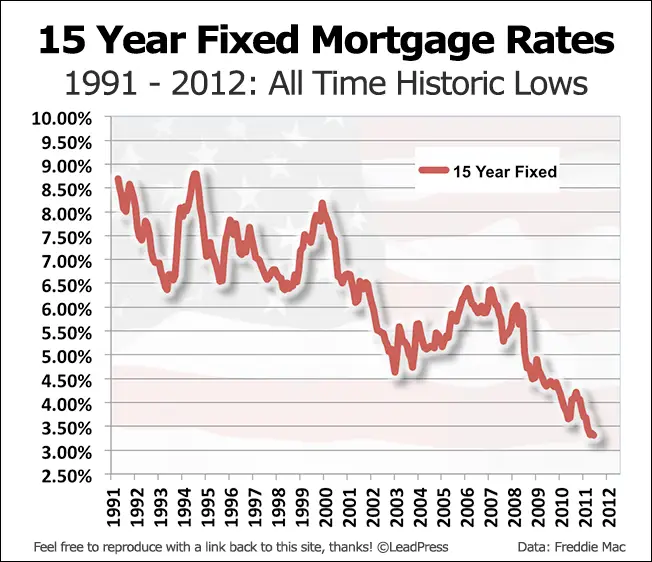
Historical Mortgage Rates Chart
Despite recent rises, todays 30-year mortgage rates are still below average from a historical perspective.
Freddie Mac the main industry source for mortgage rates has been keeping records since 1971. Between April 1971 and August 2022, 30-year fixed-rate mortgages averaged 7.76 percent.
So even with the 30-year FRM above 5%, todays rates are still relatively affordable compared to historical mortgage rates.
How Historical Mortgage Rates Affect Home Purchases
Lower mortgage interest rates encourage home buying. Low rates mean less money paid in interest. This translates to a lower payment. Mortgage lenders determine how much you can borrow by comparing your income to your payment. With a lower monthly payment, you may be able to afford more house.
Even if rates slightly rise, an adjustable rate mortgage can still offer extremely low mortgage rates. The interest rates on ARMs adjust over a period of time. You may be able to get into a lower-rated ARM now, then change the loan before it adjusts. Talk to your lender about the possibility of converting your ARM to a FRM if rates go lower.
Recommended Reading: How Much Would A 70000 Mortgage Cost
Economic Data From The Week
It was a relatively busy first half of the week on the U.S economic calendar. Key stats included ISM Manufacturing PMI and finalized Markit survey private sector PMIs. On the labor market front, JOLTs job openings and ADP nonfarm payrolls also drew interest.
The stats were skewed to the negative, with the private sector seeing slower growth in December. In spite of the fall in the PMIs, the numbers were not weak enough to raise any red flags.
JOLTs job openings for November had also disappointed ahead of the ADP nonfarm employment change figures on Wednesday, which impressed.
In December, nonfarm payrolls jumped by 800,000 according to the ADP. Economists had forecast a more modest 400k rise.
While the stats drew plenty of interest, it was the FOMC meeting minutes that drive yields northwards. A more hawkish than anticipated set of minutes that pointed to a more aggressive removal of policy support drove mortgage rates northwards.
Mortgage Rates In The 2000s
At the start of the 2000s, mortgage rates averaged around 8% and then gradually fell to a range of 5% to 6% for most of the decade.
This was also a significant decade for mortgage rates because of the 2008 financial crisis, causing the Federal Reserve to slash its federal funds rate to near 0 to make borrowing more affordable. By the end of 2009, the average rate on a 30-year fixed mortgage was around 5.14%.
You May Like: How Do You Work Out Monthly Mortgage Payments
Why Mortgage Rates Once Reached A Sky
Imagine paying over 18% interest on a 30-year fixed mortgage. Its almost unthinkable. But that was the reality for home buyers in a year when the average rate was almost 17%.
Unlike today, in the early 1980s, the Federal Reserve was waging a war with inflation. In an effort to tame double-digit inflation, the central bank drove interest rates higher. As a result, mortgage rates topped out at 18.45%.
In this Just Explain It, well take a look at how mortgage rates affect home loan payments, and show you what you can do to save money.
Back in the early 1980s, high interest rates had a negative effect on the housing market. Affordability dropped to an all-time low as rates climbed to record levels. Simply put, mortgage rates priced most Americans out of the market, and it took years for home sales to rebound. Today, rates are historically low for a number of reasons, thanks in large part to the Federal Reserve which has gone to great lengths to keep rates down to facilitate economic recovery.
According to the Census Bureau, the average cost of a home in 1981 was $82,500. With an interest rate of 18.45%, buying a home was expensive. A monthly payment, after putting 20% down, would have been $1,019. That’s the equivalent of $2,500 today, adjusting for inflation. And that doesnt include property taxes, home insurance, etc.
In both cases, 82% of your payments over 30 years would go towards interest.
Related:Average US Rate on 30-year Mortgage at 4.35 pct
How Mortgage Rates Affect Home Prices
As historical mortgage rates have swung back and forth, homebuyers have been forced to face the consequences. Not only do changing interest rates have an impact on monthly budgets, but also the number of potential home shoppers.
In many instances, low interest rates have caused an increase in home buyers because homes become more affordable. With an increase in interested buyers, the demand typically tends to push home prices higher. However, it is important to note that this general correlation doesn’t always appear based on unique economic circumstances.
For example, during the Great Recession, there was a period of time when interest rates and prices fell in tandem. With the numerous factors affecting home prices, mortgage rates are not the only piece of the puzzle.
With dropping interest rates throughout 2020, the real estate market saw a dramatic rise in home prices. As mortgage rates fell, buyers were able to fit a larger mortgage into their monthly budget. In fact, the median home price rose from $270,400 in February 2020 to $313,000 in February 2021.
Let’s consider how a potential home buyer with a monthly budget of $1,500 would be affected by changing interest rates. With a fixed-rate of 3% on a 30-year mortgage, this homebuyer could afford a $355,000 home. But if the interest rates rose to 6%, the same buyer would only be able to afford a $250,000 home. It is clear to see that changing interest rates can have a big impact on your home shopping budget.
Don’t Miss: How To Calculate Mortgage Eligibility
What Is The Difference Between The Interest Rate And Apr On A Mortgage
Borrowers often mix up interest rates and an annual percentage rate . Thats understandable since both rates refer to how much youll pay for the loan. While similar in nature, the terms are not synonymous.
An interest rate is what a lender will charge on the principal amount being borrowed. Think of it as the basic cost of borrowing money for a home purchase.
An represents the total cost of borrowing the money and includes the interest rate plus any fees, associated with generating the loan. The APR will always be higher than the interest rate.
For example, a $300,000 loan with a 3.1% interest rate and $2,100 worth of fees would have an APR of 3.169%.
When comparing rates from different lenders, look at both the APR and the interest rate. The APR will represent the true cost over the full term of the loan, but youll also need to consider what youre able to pay upfront versus over time.
The 1979 Conservative Government
The incoming administration of Margaret Thatcher raised interest rates to 17 per cent, as the government of the time saw this as a critical weapon in combating inflation, which was steadily rising at the time. It did have the effect of reducing inflation, although critics noted its negative impact on UK manufacturing exports. Interest rates began to rise again towards the end of the 1980s, partly under the pressure of house price rises. Interest rates had gone from 17% in 1979 down to 9% in 1982, and were back to 14.88% in October 1989.
Don’t Miss: What Is The Payment On A 140 000 Mortgage
What Are The Historic Mortgage Rates In The Uk
Until July 2016, the base rate has remained stable at 0.5%. Between then and the Coronavirus outbreak, it dropped to 0.25%, rose to 0.75%, then dropped again to todays rate. As a result, mortgage rates have been affected.
The highest the UK base rate has been in recent memory was 17% in the late 70s, when rising wages and oil prices were causing a surge in inflation. However, the UK base rate was also very high in the early 90s when it averaged around 15%.
On the flip side, some of the biggest drops were in 1992 when UK interest rates fell 9% on Black Wednesday and in 2008 when they dropped 5.25% due to the financial crisis.
The new 2021 decrease represents an unprecedented low for the base interest rate. As mortgage interest rates generally reflect that of the Bank of England Base rate, this means the interest you pay if you take out a mortgage in the current climate may also be unusually low.
A Brief History Of Mortgage Rates
The history of mortgage rates dates back to ancient India, where buyers and sellers exchanged an agreement where the seller would provide a piece of land or property in exchange for financial compensation
The property owner had an out, however. If the mortgage recipient couldn’t hold up his end of the bargain, the agreement was legally null and void – and the borrower would have to start looking for another place to live.
Both ancient Greece and Rome also planted the seeds for mortgages, and mortgage interest, when the concept of debt was introduced to the home ownership equation. That scenario saw the mortgage recipient living on a property owned by the mortgage provider, until the agreed-upon debt was paid off.
It was at that time the term mortgage first found its way into the regional economic vernacular.
The term itself has Latin roots, with the term “mortgage” stemming from two separate terms – “mortuus” and “gage” Combining the two terms into a single word may not have intentionally been designed to send the “death pledge” message, but it’s understandable that property buyers may have taken it that way
Don’t Miss: How To Lock Mortgage Rate For 6 Months
Us Mortgage Interest Rates Rise To Highest Level Since 2006
– The average interest rate on the most popular U.S. home loan rose to its highest level since 2006 as the housing sector continued to bear the brunt of tightening financial conditions, data from the Mortgage Bankers Association showed on Wednesday.
Mortgage rates have more than doubled since the beginning of the year as the Federal Reserve pursues an aggressive path of interest rate hikes to bring down stubbornly high inflation.
Those actions, designed to cool the economy sufficiently to curb price pressures, have weighed heavily on the interest-rate-sensitive housing sector as expectations for Fed tightening have led to a surge in Treasury yields. The yield on the 10-year note acts as a benchmark for mortgage rates.
The average contract rate on a 30-year fixed-rate mortgage rose by 6 basis points to 6.81% for the week ended Oct. 7 while the MBA’s Market Composite Index, a measure of mortgage loan application volume, fell 2.0% from a week earlier and is down roughly 69% from one year ago.
Its Purchase Index, a measure of all mortgage loan applications for purchase of a single family home, fell 2.1% from the prior week and is 39% lower than a year ago, while MBA’s refinance Index declined 1.8% last week and is down 86% from one year ago.
Adjustable Rates Vs 30
Freddie Mac began to record the average interest rates for 5-year Adjustable-Rate Mortgages in 2005. With that, the table below reflects a comparison between 30-year fixed-rate mortgage rates and 5-year Adjustable-Rate mortgages with a 30-year term starting in 2005.
Adjustable-rate mortgages can provide the opportunity to save money on interest in the short term. However, rate fluctuations can make it difficult to budget for your future mortgage payment beyond the first five years.
Don’t Miss: Does Charles Schwab Offer Mortgages