What Led To The High Interest Rates Of The 1980s
Question: What were the causes and circumstances that led to the high interest rates in the 80s? Was it inability to effect a change or inaction in addressing the issue?
Paul Solman: If by interest rates you mean the rate set by the Fed the Fed funds rate it rose to TWENTYPERCENT in 1980. But no, it was not inaction but just the opposite: a deliberate rise in rates triggered by inflation.
Lets take a step back for a moment. In general, over the long haul, interest rates are determined by the market. Think of a market interest rate as the sum of three separate factors: waiting, repayment risk, and inflation.
First, waiting also known as the time value of money. Imagine an inflation-free environment, such as todays. Which would you take: a thousand dollars today or a thousand dollars, guaranteed, a year from now? Unless youre a very unusual person, its the thousand right now, so you can do something with the money. If you forgo the money, you generally need to be paid something for doing so, for waiting in recent history, around 2 percent a year.
Second is the risk of not being paid back. This is why folks with low FICO scores have to pay such high rates of interest. This obviously varies enormously. But the U.S. government has generally been thought to pay the risk-free rate: 0 percent for risk.
The rest of the interest rate is inflation. If money is losing value and you lend it, youre going to expect to be reimbursed for the loss.
Historical Mortgage Rates Chart: Trends Over Time
Despite recent rises, todays 30year mortgage rates are still ultralow from a historical perspective.
Freddie Mac the main industry source for mortgage rates has been keeping records since 1971.
Between 1971 and December 2020, 30year mortgage rates averaged 7.89%.
But between January and October of 2021, they averaged just 2.93%.
Even if rates keep rising, many experts predict they wont go above 4% in 2022. That means home buyers and homeowners should keep enjoying rates that are about half the historical average.
History Making Canadian Interest Rates
For a while now weve been reading headlines about how interest rates are at historic lows. Which is great news for anyone with a variable-rate mortgage, line of credit debt, or who is looking to negotiate for things like car loans or fixed-rate mortgages.
But whats the other extreme? How high have and could interest rates go, and what would it mean to your savings if they did?
Heres a quick walk through the history of interest rates in Canada and abroad.
You May Like: 70000 Mortgage Over 30 Years
Mortgage Rate Trends In The 1980s
The 30-year fixed mortgage rate reached a pinnacle of 18.4 percent in October 1981, according to Freddie Mac, seesawing down to the 9 percent range by 1986 and closing the decade at 9.78 percent. The 1970s oil embargo against the U.S., which drove up inflation quickly, contributed to the increased borrowing costs.
How Global Events Have Shaped Rates
U.S. president Richard Nixon cuts U.S. dollars link with gold, letting the currency float freely
Arab oil embargo causes crude-oil prices to quadruple
Pierre Trudeau government introduces wage and price controls under the Anti-Inflation Act
Early 1978: Wage and price controls are phased out in Canada
The Shah of Iran is overthrown and revolutionary government cuts oil production prices soar
Early 1980: U.S. Fed chair Paul Volcker pushes up rates and tightens money supply to fight inflation
Canadian five-year mortgage rate peaks at more than 21 per cent
Early 1982: North American economy begins to improve and inflation slips
Five-year mortgage rate in Canada falls below 10 per cent for the first time since 1973
The Asian Contagion, a financial crisis primarily centred in Asia, begins with the collapse of the Thai Baht
Fed chair Alan Greenspan cuts U.S. rates to keep the Asian financial crisis from affecting the U.S. economy
Worry over Y2K, a potential computer bug resulting from the shift to a new millennium, causes uncertainty in global markets
The U.S. financial crisis spreads around the globe after the bankruptcy of Lehman Bros.
Bank of Canada becomes the first G7 central bank to raise rates after the recession
Read Also: What Does Gmfs Mortgage Stand For
Early History Of The Mortgage
The modern mortgage has only been around since the 1930s, but the idea of a mortgage has been around for a lot longer.
First, its important to talk about the meaning of the word mortgage. To understand the word, we need to break it down into two separate Latin words: mort and gage. Mort means death and gage means pledge. A mortgage is a dead pledge.
Dont let that scare you! The dead part of the mortgage doesnt refer to you or any other person. Instead, it refers to the idea that the pledge died once the loan was repaid, and also the idea that the property was dead if the loan wasnt repaid.
Mortgages are mentioned in English common law documents that take back as far as 1190. These documents illustrate the beginnings of a basic mortgage system. They describe how a creditor is protected in property purchase agreements. Specifically, a mortgage was a conditional sale where the creditor held the title to the property while the debtor could sell that property in order to recover the money paid.Essentially, a mortgage is a loan secured by a property. Most people dont have the liquid capital required to purchase a house entirely on its own and mortgages help these people purchase homes and properties.
Mortgage Rate Predictions For 2021
At the time of this writing , the U.S. economy was in a strong growth period coming out of the pandemic. And the Fed had just announced plans to start withdrawing its mortgage stimulus, pushing interest rates higher.
Inflation was also at a 30year high. And rising inflation tends to drag rates up with it.
In short, all signs point toward higher rates in 2022 as the economy continues to expand.
So dont wait on lower 30year interest rates. They could fall for short periods of time, but were likely to see an overall upward trend in the coming months.
Don’t Miss: Chase Mortgage Recast Fee
Could This Happen Again And What Implications Would It Have
Millennials should count themselves lucky for coming of age well after the harrowing economic events of the late 70s and early 80s. It might be hard to conceive in todays benign environment, but in late 1981, 30-year mortgage interest rates topped out at 18.45 percent, killing the housing market as financing became unaffordable. Are we in that kind of environment now? No. Could it happen again? Undoubtedly.
Mortgage Rate Trends In The 2000s
The 30-year rate took another tumble in the latter half of the 2000s when the housing market crashed due to the prevalence of subprime loans. According to Bankrates data, the average 30-year fixed mortgage rate dropped from about 8 percent at the start of the decade down to 5.4 percent by 2009, when the Federal Reserve implementedquantitative easing, buying mortgage bonds in bulk to drive down interest rates and usher in an economic recovery.
Don’t Miss: Recasting Mortgage Chase
Runaway Inflation Kills Housing
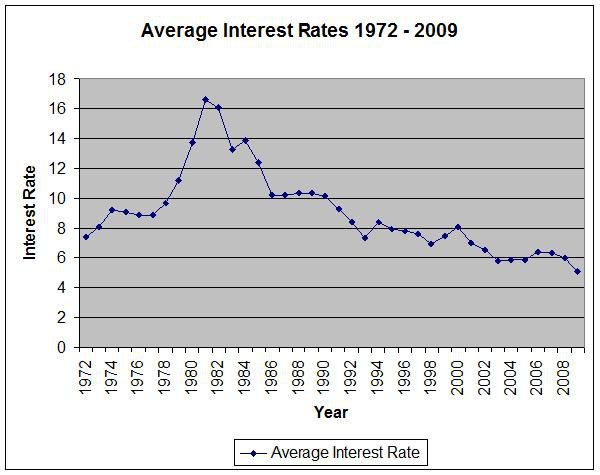
The reason interest rates, which ultimately are set by the Federal Reserve, exploded in 1980 was housings arch nemesis, runaway inflation. The Fed funds rate, which is the rate banks charge each other for overnight loans, hit 20 percent in 1980, and 21 percent in June 1981. The cause was an inflationary spiral brought on by rising oil prices, government overspending and rising wages. All three factors pushed the general price of goods and services higher, which is the definition of inflation.
The First Mortgages In America
The idea of a mortgage started in England and moved throughout the western world from 1190 onward. In the late 1800s and early 1900s, Americas waves of immigrants increased the need for mortgages and affordable property.
Unfortunately, mortgages at the turn of the century were different from mortgages today. In the early 1900s, homebuyers typically had to pay a 50% down payment with a 5 year amortization period. This meant that those who bought a house or property typically already had a lot of money. If you were buying a $100,000 house, you would have to pay $50,000 and pay off the remaining $50,000 within 5 years.
Increasing the likelihood of default was the fact that mortgages were structured completely differently than modern mortgages. On a 5 year mortgage, homebuyers would pay interest-only payments for the 5 year term. At the end of the 5 years, they would face a balloon payment with the entire principal of the loan.
This system wasnt perfect, but it did provide homes and properties to millions of Americans. However, once the Great Depression hit, mortgages would never be the same again. During the Great Depression, lenders had no money to lend of course, borrowers didnt have any money to pay for the hard-to-find loans either.
Don’t Miss: Reverse Mortgage For Condominiums
Year Mortgage Rates Chart: Where Are Rates Now
Mortgage interest rates fell to record lows in 2020 and 2021 during the Covid pandemic.
Emergency actions by the Federal Reserve helped to push mortgage rates below 3% and keep them low.
But, with the economy in recovery mode, mortgage interest rates have risen since their alltime low in January 2021. And theyre likely to keep rising in 2022.
Mortgage Rate Trends In The 1970s
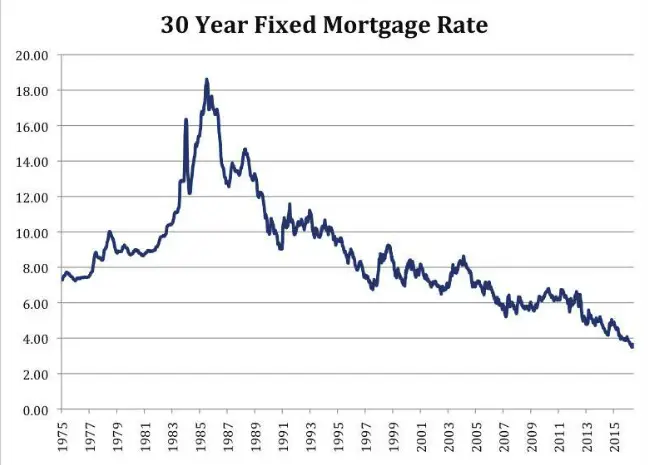
The 30-year fixed-rate mortgage started off the decade at about 7.3 percent in 1971, according to Freddie Mac. By the end of 1979, in a time of heightening inflation, that rate rose to 12.9 percent. While inflation doesnt directly influence mortgage rates, if it rises too fast and wages dont keep up, borrowers have less purchasing power overall.
You May Like: Monthly Mortgage On 1 Million
How Historical Mortgage Rates Affect Homebuying
When mortgage rates are lower, buying a home is more affordable. A lower payment may also help you qualify for a more expensive home. The Consumer Financial Protection Bureau recommends keeping your total debt, including your mortgage, to 43% of what you earn before taxes .
When rates are higher, an ARM may give you temporary payment relief if you plan to sell or refinance before the loan resets. Ask your lender about convertible-ARM options that allow you to convert your loan to a fixed-rate mortgage without having to refinance before the fixed-rate period expires.
What Big Events Happened In The 80s
1980s
- Ronald Reagan Elected President. CNN Begins Broadcasting.
- Sandra Day OConnor First Woman U.S. Supreme Court Justice. Iranian Hostages Released.
- Falklands War.
- Sally Ride First U.S. Woman Astronaut.
- Macintosh Computer.
- Mikhail Gorbachev Institutes Glasnost and Perestroika in USSR.
- Challenger Explodes.
Don’t Miss: Recast Mortgage Chase
Mortgage Rates In 2020 And 2021
2020 saw new lows for mortgage rates, with the 30-year fixed rate diving to just under 3 percent, according to Bankrate data, and averaging 3.38 percent for the year. Amid the pandemic, fearful investors were attracted to safer products such as Treasury and mortgage bonds, pushing yields and rates lower, explains McBride.
The onset of the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020 spurred mortgage rates to new record lows, as the economy was faced initially with a rapid contraction that was the worst since the Great Depression and followed up by unprecedented accommodation by the Federal Reserve, McBride says.
While rates ticked up slightly in 2021, that trend has since reversed, and the 30-year fixed rate continues to hover at a low point: 3.2 percent as of early August 2021. You can view current 30-year mortgage rates on Bankrate.
Is It Smart To Pay Off Your House
If youre focused on paying off your mortgage, good for you. Its generally always good to get rid of debt. And with interest rates at all-time lows, it might make more sense to refinance your mortgage into a low fixed-rate term for as long as you plan to own the property and then invest the rest.
Read Also: Does Rocket Mortgage Service Their Own Loans
Bankstats Articleby Hannah Phaup
The Bank of England compiles and publishes mortgage interest rate statistics starting with 1995 data. But other sources of mortgage rates data, which could be used to supplement these statistics, are available from the One Bank Research data sets compiled by the Bank of England. A new tranche of data was added recently, extending the mortgage rates back to 1853.
How Historical Mortgage Rates Affect Buying A Home
Broadly speaking, lower mortgage rates fuel demand among homebuyers and can increase an individuals buying power. A higher rate, on the other hand, means higher monthly mortgage payments, which can be a barrier for a buyer if the cost becomes unaffordable. In general, a borrower with a higher credit score, stable income and a sizable down payment qualifies for the lowest rates.
Don’t Miss: Reverse Mortgage On Condo
How We Make Money
You have money questions. Bankrate has answers. Our experts have been helping you master your money for over four decades. We continually strive to provide consumers with the expert advice and tools needed to succeed throughout lifes financial journey.
Bankrate follows a strict editorial policy, so you can trust that our content is honest and accurate. Our award-winning editors and reporters create honest and accurate content to help you make the right financial decisions. The content created by our editorial staff is objective, factual, and not influenced by our advertisers.
Were transparent about how we are able to bring quality content, competitive rates, and useful tools to you by explaining how we make money.
Bankrate.com is an independent, advertising-supported publisher and comparison service. We are compensated in exchange for placement of sponsored products and, services, or by you clicking on certain links posted on our site. Therefore, this compensation may impact how, where and in what order products appear within listing categories. Other factors, such as our own proprietary website rules and whether a product is offered in your area or at your self-selected credit score range can also impact how and where products appear on this site. While we strive to provide a wide range offers, Bankrate does not include information about every financial or credit product or service.
S And The Creation Of Freddie Mac
As Baby Boomers grew older, their housing demands increased. They wanted to purchase larger and more expensive homes. Unfortunately, the mortgage market didnt quite have enough capital available to finance the needs of these homebuyers.
Thats where Freddie Mac comes in. In 1970, the U.S. Congress created an organization called the Federal Home Loan Mortgage Corporation . Today, we know that organization as Freddie Mac. The organization was designed to increase the amount of financial capital available to mortgage lenders and, by extension, borrowers.
To do that, Freddie Mac operated in a similar way to Fannie Mae. The organization purchased mortgages from lenders, giving them more capital to spend on more mortgages. Freddie Mac is also well-known for offering 30 year fixed-rate mortgages, giving buyers the opportunity to lock in a mortgage at a lower interest rate in order to hedge their bets against rising interest rates in the future.
At the same time, interest rates were rapidly rising. Interest rates rose sharply throughout the 1970s and 1980s and eventually rose above 20%. In previous years, lenders were happy to provide mortgages with 20 to 30 year periods, but during this period of exceptionally high interest rates, most mortgages included 1 year, 3 year, or 5 year terms. It wasnt until the late 1990s that interest rates finally fell below 7%.
Don’t Miss: Reverse Mortgage Mobile Home
What Ended The 1982 Recession
Canadas inflation rate was 10.2% for 1980 overall, rising to 12.5% for 1981 and 10.8% for 1982 before dropping to 5.8% for 1983. Canadas GDP increased markedly in November 1982 officially ending the recession, although employment growth did not resume until December 1982 before faltering again in 1983.
What Moves Interest Rates
When you examine interest rates closely, you encounter three main reasons they are what they are:
Also Check: How Much Is Mortgage On A 1 Million Dollar House
Mortgage Rate History: Check Out These Charts From The Early 1900s
Today well take a brief look at some mortgage rate history to gain a little context. Its always helpful to know what came before so you can better guess what might come after.
Just about everyone knows that mortgage rates hit all-time record lows over the past year. But do you know what mortgage rates were like in the 1900s?
The 30-year fixed averaged 3.31% during the week ending November 21, 2012, its lowest point in history.
Later, the 15-year fixed hit the lowest point ever, sinking to 2.56% during the week ending May 2, 2013.
