Mainstreet Explains: What Is A Conforming Mortgage
When buying a home or refinancing, it pays to conform.
With all the dreadful news and market action on banks home and abroad over the past few days, we need to remember that life goes on, and its possible to find some benefit in the current environment.
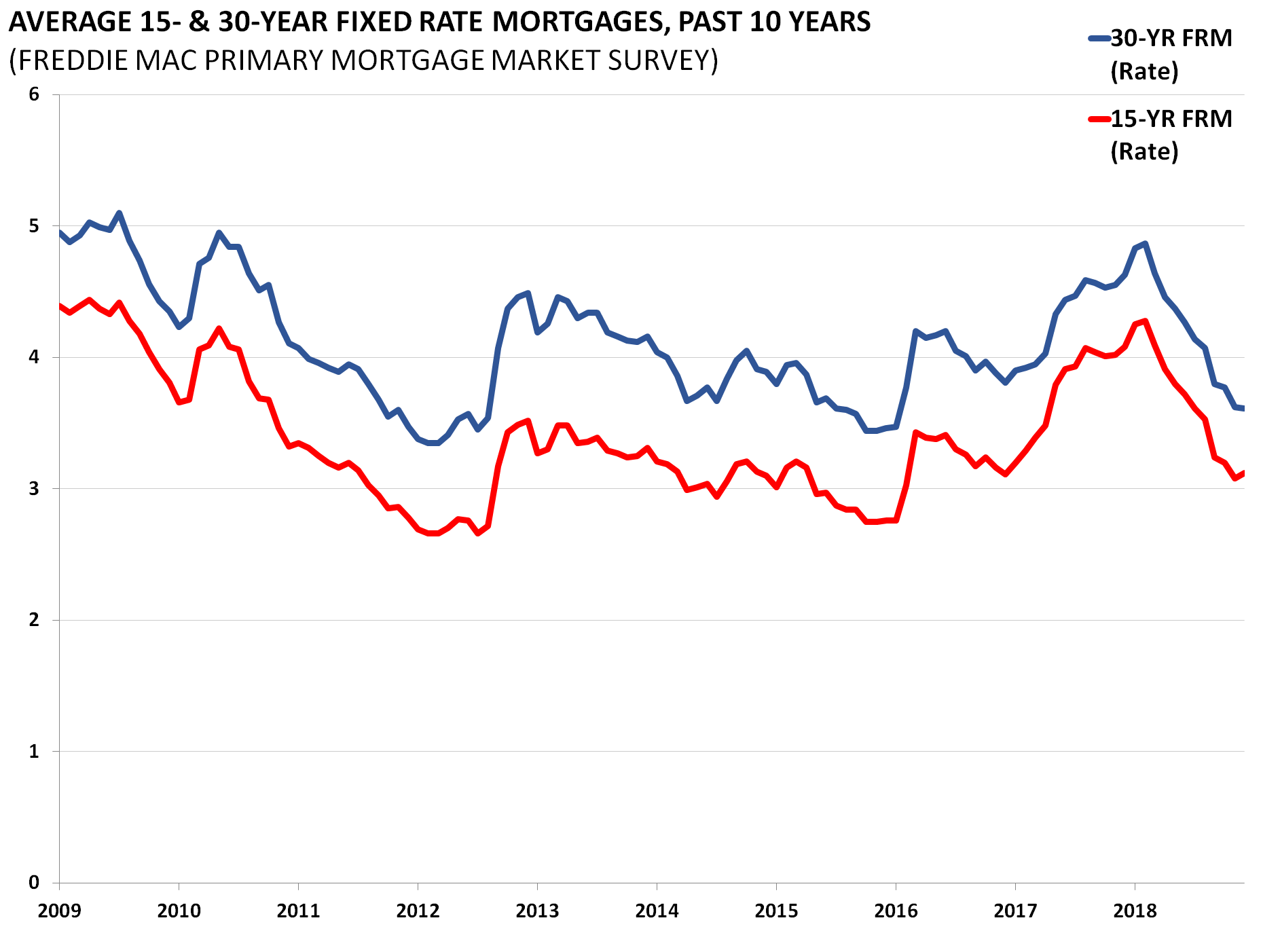
With the federal funds target rate lowered on Dec. 16 to a floating range between 0% and 0.25% and prime to 3.25%, mortgage rates have dropped dramatically over the past month. As expected, this and the freefall of home prices in areas like California have led to an increase in mortgage applications for home purchases.
Refinancing activity has picked up as well. However, with so many people upside down, or owning mortgages that exceed the market values of their homes, refinancing isnt an option for everyone.
According to the Mortgage Bankers Association survey for the week of Jan. 15, mortgage application volume increased 96% from the previous week and 52% from the same week a year earlier.
On Wednesday, BankingMyWays composite index for 30-year fixed-rate mortgages was 5.15% and 4.88% for a 15-year fixed.
The variable rate indexes were considerably higher. Its best to stay away from variable-rate loans anyway because of the additional risk if rates increase. Theres considerable risk of a drawn-out, painful increase in interest rates at some point, since the federal government is borrowing so much money to bail out banks and other companies, as well as to stimulate the economy while tax revenues are declining.
The Bottom Line: Conforming Loans Offer Lower Interest And Greater Consumer Protections
Conforming loans are typically preferred by those seeking to avoid paying a high interest rate, and represent the largest sector of home loans. Want to learn more about how to shop around for the best mortgage? Our Learning Center has all the information you need as you move through the home buying process.. If youre interested in going over your options, you can apply online or give us a call at 452-0335.
Benefits Of Conforming Loans
Conforming mortgage loans certainly have some benefits over their non-conforming counterparts.
For starters, conforming mortgage loans have fairly standard qualification requirements. While Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac are two separate entities, their underwriting criteria and eligibility requirements align very closely.
While individual lenders may have additional underwriting overlays, in general most conforming loans require similar criteria for approval. This also simplifies the comparison process if borrowers want to shop lenders to find the best rate and repayment terms.
Additionally, conforming conventional loans are probably the most widely offered solution that consumers can take advantage of. This is partially due to the fact that these loans carry less risk, as they are being sold off into the secondary market as opposed to remaining on the lenders books.
Since there are a multitude of lenders that offer conforming conventional mortgage loans, consumers have more choices on who they want to do business with.
Lastly, while it is not always the case, in general conforming mortgages can often offer a lower interest rate compared to other non-conforming options.
You May Like: Rocket Mortgage Qualifications
Size And Location Affect Conforming Limits
Conforming limits in Alaska, Guam, Hawaii and the U.S. Virgin Islands are higher than in the continental U.S. due to the cost of building and financing homes in these areas. Also, certain counties within the U.S. are considered high cost and have higher conforming loan limits. In 2014, there were 18 high cost areas, including pricey California coastal areas of San Diego, San Francisco and Los Angeles and New York, Newark and New Jersey. Increased conforming limits also apply to two-, three- and four-unit properties.
What Does It Mean To Conform
A conforming loan is one that meets certain pre-established criteria used by Freddie Mac and Fannie Mae. The most important of these criteria is the size or amount of the loan.
When a borrower uses a mortgage that falls within the loan limits for his or her county, it is referred to as a conforming loan. It can therefore be sold to Fannie Mae or Freddie Mac via the secondary mortgage market.
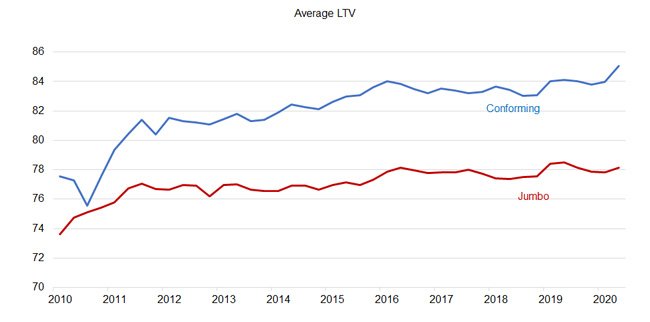
When a conventional home loan exceeds the conforming limits for the county where the home is being purchased, it is referred to as a jumbo loan. This means it does not meet the conforming standards used by Fannie and Freddie, and therefore cannot be sold to either of those entities.
Because of the larger amount being borrowed, jumbo loans are typically more strict in terms of borrower eligibility criteria. Generally speaking, borrowers need better credit and a larger down payment in order to qualify for a jumbo mortgage product.
So, from a size perspective, a conventional loan can either be conforming or jumbo. If it falls within the parameters used by Freddie Mac and Fannie Mae , it is considered to be a conventional conforming loan.
On the other hand, if it exceeds the size limits or other parameters used by Freddie and Fannie, it is referred to as a jumbo loan.
Don’t Miss: How Much Is Mortgage On A 1 Million Dollar House
Conforming Loans Vs Other Types Of Mortgages
A conforming loan is a type of conventional loan, but you don’t necessarily need to get a conventional mortgage. Instead, you may opt for a government-backed mortgage.
Each type of government loan has its own eligibility requirements. There are three main types of government-backed mortgages:
- FHA loans: You can get a mortgage with a lower credit score and higher DTI than with a conforming loan, and you’ll need a 3.5% down payment.
- VA loans: Military families can get VA loans with no down payment.
- USDA loans: You can buy a home with no down payment if you have a low-to-moderate income and are buying in a rural or suburban area.
You may find that one of these types of mortgages is a better fit than a conventional mortgage, even if you’re borrowing an amount that qualifies you for a conforming loan.
Fha Mortgage Vs Conforming Mortgage : A Cheat Sheet
With so much difference between the FHA and conforming 30-year fixed rate mortgage, theres no set playbook for choosing the best mortgage. The math will depend on your particular purchase and planned budget.
For example, if you need to make as small of a downpayment as possible, youll want to choose the FHA. Its 3.5% downpayment program is bested only by the for military borrowers, and the USDAs for suburban and rural homes.
However, as a starting point for comparisons between FHA and conforming mortgages :
- Downpayment of 4.99% or less : Apply for an FHA mortgage
- Downpayment of 5.00-19.99% : Ask your loan officer for a recommendation
- Downpayment of 20% or more : Apply for a conforming mortgage
These guides have exceptions, of course. A 15-year fixed rate mortgage carries different considerations, for example, as does a home bought at a steal.
Talk with your loan officer about choosing your optimal route.
Read Also: Can I Get A Reverse Mortgage On A Condo
Conforming Vs Conventional Loans
If you have ever applied for a mortgage, you may have heard lenders refer to loans and wonder what is the difference between conforming vs conventional loans?
But if you are a mortgage lender, you are fully aware that referring to a loan and know the differences between conforming vs conventional, knowing doesnt always mean the same thing.
A lot of confusion around conforming mortgages stems from the fact that only conventional loans can be conforming loans. However, not all conventional loans are conforming mortgages.
So, what makes a loan a conventional loan and what makes it a conforming loan? Can a conventional loan be conforming?
Below we will discuss the differences between conforming vs conventional mortgage loans.
New Rules Limit The Types Of Mortgages The Enterprises Will Buy
The Recession also helped the FHFA, Federal Housing Financing Agency, mandate Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac to require their lenders to comply with all CFPB consumer protections. This is in addition to any Fannie Mae or Freddie Mac rules.
Private lenders are still free to create their own rules and originate non-conforming loans, but Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac cannot buy them.
Also Check: Rocket Mortgage Loan Requirements
The Six Main Types Of Mortgages
Not all mortgage products are created equal. Some have more stringent guidelines than others. Some lenders might require a 20% down payment, while others require as little as 3% of the homes purchase price. To qualify for some types of loans, you need pristine credit. Others are geared toward borrowers with less-than-stellar credit.
The U.S. government isnt a lender, but it does guarantee certain types of loans that meet stringent eligibility requirements for income, loan limits, and geographic areas. Heres a rundown of various possible mortgage loans.
Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac are two government-sponsored enterprises that buy and sell most of the conventional mortgages in the U.S.
Jumbo Loans: The Most Common Nonconforming Loan
A jumbo loan is a high-value loan that exceeds the GSEs conforming loan limits, which are typically lower than non-conforming loan rates. These are the most common type of nonconforming loan.
But jumbo loans commonplace in the more expensive metropolitan areas of the country increasingly have interest rates comparable to conforming loans. Limits on jumbo loans vary by lender.
Jumbo loan down payments required will vary depending on loan amount and credit score. You may need 10.01% down to qualify.
Lenders will carefully look at your finances and cash reserves before they give you a loan. Your lender may require you to have up to 12 months of mortgage payments in your savings account before you can get a loan. Youll also need a higher credit score compared to other loan types.
Also Check: Can You Get A Reverse Mortgage On A Condo
How Does This Affect My Homebuying Process
Most buyers, especially for their first home, count on a low down payment and favorable interest rates to make the purchase affordable. Those perks are easier to access with a conforming loan.
So before you begin your home search in earnest, make sure you check on the loan limits for your area . This will serve as a benchmark for which homes you can purchase with less than 20% down payment and relatively easier requirements.
Be aware of how the limits change from county to county, because you might end up in jumbo loan territory without realizing it. For example, the loan limit in Monmouth County, New Jersey, is $822,375. But cross the border into Mercer County, and the limit drops back down to $548,250,
If youre anywhere near that edge and you think you might go over, you need to see if you qualify for jumbo, said Beeston.
If you do end up needing a non-conforming loan, thats okay. Youll just need to make sure youve got the cash to afford the higher down payment and reserve requirements.
When Does The Conforming Loan Limit Change
- The conforming loan limit doesnt change every year
- But any upcoming changes are announced in November
- Based on October-to-October home price movement
- New loan limits go into effect the following January
The conforming loan limit changes annually, as determined by the FHFA, based on October-to-October home price data. It is announced in November and goes into effect the following January.
The Emergency Home Finance Act of 1970 originally established a conforming loan limit of $33,000 for Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac.
Congress later raised the conforming limit to $60,000 for mortgages originated in 1977, and pushed it to $67,500 in 1979.
Not long after, the Housing and Community Development Act of 1980 increased the loan limit to $93,750 and tied future increases to changes in national home prices.
This legislation also established loan limits for two, three, and four-unit properties.
The conforming loan limit has risen substantially in the past thirty years as housing prices have skyrocketed in the United States, but a good chunk of mortgages in major metropolitan areas are still designated as jumbo loans because the data tends to lag.
Below are the 2021 conforming loan limits for properties in the contiguous United States:
One-unit properties: $548,250Three-unit properties: $848,500Four-unit properties: $1,054,500
*For one-unit properties in Alaska, Hawaii, Guam, and the U.S. Virgin Islands, the conforming loan limit is $822,375, which is 50% higher than the baseline.
Read Also: Can You Get A Reverse Mortgage On A Mobile Home
Conforming Loans Vs Super Loans How Do They Work
The Federal Mortgage National Association and Federal Home Loan Mortgage Corporation are federally backed home mortgage companies that drive the market for home loans. The corporations buy mortgages that banks and other lender unions give out.
What happens is that banks, credit unions, and other lending agencies purchase properties on their behalf and transfer the ownership to the borrowers. In return, borrowers promise to pay back the lender with interest. It means that Frannie Mae and Freddie Mac works as secondary market makers as mortgages are not issued by them.
These government agencies have set the maximum loan amounts, income requirements, borrowing limits, suitable properties, and down payment. In other words, conforming rules set for how to qualify for a mortgage and much the borrowers can borrow. New loan limits are announced by the corporations each year to reflect the change in the national average cost of a home. The borrowing limit means that you cant borrow the maximum amount set by Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac.
Both super loans and conforming loans offer the same guarantees to the lenders. However, super rates are usually available in fixed rates or adjustable rate forms. With certain programs, the down payment is as low as 5%. The jumbo loan limits can range up to $ 2 million, whereas the super loan limits cannot exceed the limit of the high-cost area that the property is located in.
How Does A Nonconforming Loan Work
Nonconforming loans don’t meet Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac purchase guidelines. If you don’t qualify for a conforming loan, you’ll need a lender that offers alternatives.
There are many types of nonconforming loans. These include:
- A subprime loan
- A jumbo loan with higher loan limits
- Government-backed loans such as an FHA loan, VA loan, or USDA loan
The requirements for nonconforming loans vary by loan type. For example, many lenders require larger down payments and better credit for jumbo loans because of the large loan size. In contrast, government-backed loans can be easier to qualify for. But they may come with additional fees, such as upfront funding fees for VA loans. Bad-credit home loans cater to borrows without the credentials to get a conforming loan, but interest rates are usually very high.
Recommended Reading: Rocket Mortgage Launchpad
In Which Scenarios Is The Fhlmc Fully Amortizing Fixed Rate And/or Super Conforming Loan A Good Option
Whether theyre a first-time buyer or repeat buyer, the FHLMC Fully Amortizing Fixed Rate program allows qualified borrowers to obtain competitively priced home financing with flexible underwriting standards.
A few scenarios that could be ideal for FHLMC Fully Amortizing Fixed Rate financing/refinancing include
- A borrower purchasing a single-unit primary residence who cant afford a down payment higher than 5%.
- A borrower interested in purchasing a second home.
- A current homeowner with at least 20% equity who needs cash to help pay off a big expense.
And a few scenarios that could be ideal for FHLMC Super Conforming financing/refinancing include
- A borrower purchasing a single-unit home in a high-cost area.
- A borrower who wishes to refinance their high-cost property and shorten the amortization period in order to pay off their mortgage debt sooner.
- A borrower who wishes to refinance their high-cost property and lengthen the amortization period in order to lower their monthly mortgage payments.
What Are The Pros And Cons Of Nonconforming Loans
The pros of conforming loans from the perspective of a borrower include:
If you make at least a down payment of 20%, you borrow less money and have more equity when you purchase the home. Your monthly fees can be lower than a mortgage where you put less money down.
With a down payment of at least 30%, you can avoid paying for PMI, so you can save a few hundred dollars a month, depending on your loan amount.
Borrowers who can put 20% down and have good credit are likely to qualify for the best interest rates from the lender and the lowest overall monthly payments.
The downsides of a conforming loan include that your DTI ratio has to meet the standards. The maximum DTI ratio is usually 36%, but maybe it can go as high as 50% only if you have other compensating factors like a higher credit score.
If youre in a high-priced market, especially, the home you want could very easily go beyond the loan limits, so this is also something to think about.
Also Check: How Does 10 Year Treasury Affect Mortgage Rates
What Does Conforming Mean For Mortgages
To understand conforming loans, we should first step back and give a very brief refresher on how mortgages work in particular, how mortgage companies make money. Fair warning: The acronyms are going to fly fast and furious here, so try to keep up.
Lenders often bundle multiple mortgages together as mortgage-backed securities and then sell them on the secondary market to investors. The proceeds from those transactions can then be used to fund even more home loans. Everybody wins!
Sometimes, the buyers in these transactions arent investment firms at all, but the government-sponsored entities , Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac. In fact, Fannie and Freddie are responsible for a good chunk of MBS purchase activity. But a GSE cant buy just any mortgage theyll only buy home loans that fit certain requirements. The most important criteria? The loan amount.
The Federal Housing Finance Agency sets loan limits each year, which Fannie and Freddie then need to follow. Why put restrictions on loan amounts? As with just about everything else in the mortgage industry, it has a lot to do with minimizing risk. Loan limits are tied to local housing prices, so a GSE cant buy a home loan thats significantly higher than other properties on the market. That protects GSEs, lenders and borrowers from risky mortgages.
