Refinance Options For Borrowers With A Loan To Value Ratio Over 100%
Borrowers with an extremely high loan-to-value ratio are considered upside-down on their mortgage, i.e., the value of their house is less than their loan amount. Although this is not ideal, you may still be able to refinance. Special refinancing programs exist for borrowers with a loan-to-value ratio over 100 percent. The most common high loan-to-value refinance program is the HARP Refinance program. If you have a FHA loan and have a high loan-to-value ratio, you may be eligible for a FHA streamline loan. You can shop for FHA streamline loans on Zillow. For information on other high loan-to-value loan programs please check out our underwater mortgage page.
The Importance Of Ltv
There are many reasons that your LTV matters when you are getting a mortgage. Your down payment will impact the LTV, as well as our decision to approve your mortgage. If your down payment is under 20 percent and this causes the LTV to be higher than 80 percent, for example, we will usually require private mortgage insurance if you are not getting a government-insured loan. Mortgage insurance is an additional cost you will pay, and it will be added to your monthly payment. It can be anywhere from 0.22 to 1 percent of your loan amount charged annually.
If you are required to pay PMI, it can be removed from your loan once you hit 80 percent LTV. This can happen if your home’s value increases enough, you pay down the loan earlier than expected, or you make monthly mortgage payments until you pay off the loan enough to reach this level.
Your LTV will also matter if you ever decide to refinance. When you refinance your loan, the appraised value will be used based on comparable home sales over the last three months. The LTV increases the interest rate you pay on your refinance, as homeowners who have less of their own money in the home are viewed as a higher risk. If the LTV is more than 70 percent, you can expect around a 0.125 percent increase in the interest rate for every 5 percent increase.
Ways To Potentially Increase Your Equity
If your homeâs value remains stable, you can build equity by paying down your loanâs principal. If your payments are amortized , this happens automatically, simply by making your monthly payments. To lower your LTV ratio more quickly, consider paying more than your required payment each month. This helps you chip away at your loan balance.
Also, protect the value of your home by keeping it neat and well-maintained. Smart home improvements can help, too. However, itâs a good idea to consult an appraiser or real estate professional before investing in any renovations you hope will increase your homeâs value. Remember that economic conditions â and the normal dips and swings of the real estate market â can affect your homeâs value no matter what you do. If home prices increase, your LTV ratio could drop, but falling home prices could cancel out the value of any improvements you might make.
This article was adapted from Better Money Habits®. Visit BetterMoneyHabits.com for more practical financial information.
Banking, mortgage and home equity products offered by Bank of America, N.A., and affiliated banks, Members FDIC and wholly owned subsidiaries of Bank of America Corporation. Equal Housing Lender . Credit and collateral are subject to approval. Terms and conditions apply. This is not a commitment to lend. Programs, rates, terms and conditions are subject to change without notice.
Recommended Reading: Can You Get A Reverse Mortgage On A Mobile Home
What Is A Good Ltv
If you’re taking out a conventional loan to buy a home, an LTV ratio of 80% or less is ideal. Conventional mortgages with LTV ratios greater than 80% typically require PMI, which can add tens of thousands of dollars to your payments over the life of a mortgage loan.
Some government-backed mortgages allow you to get away with very high LTV ratios. For example, the minimum down payment for a Federal Housing Administration loan is 3.5% . Loans through the U.S. Department of Agriculture and the Department of Veterans Affairs don’t require any down payment at all . Those loans typically require a forms of mortgage insurance or include extra fees in the closing costs to offset the risk connected with their higher LTVs.
LTV ratio is a less crucial factor with auto loans. While you might pay higher interest on a car loan with a higher LTV ratio, there’s no threshold comparable to the 80% LTV that earns the best mortgage loan terms.
Borrowers Can Reduce Their Ltv In A Variety Of Ways
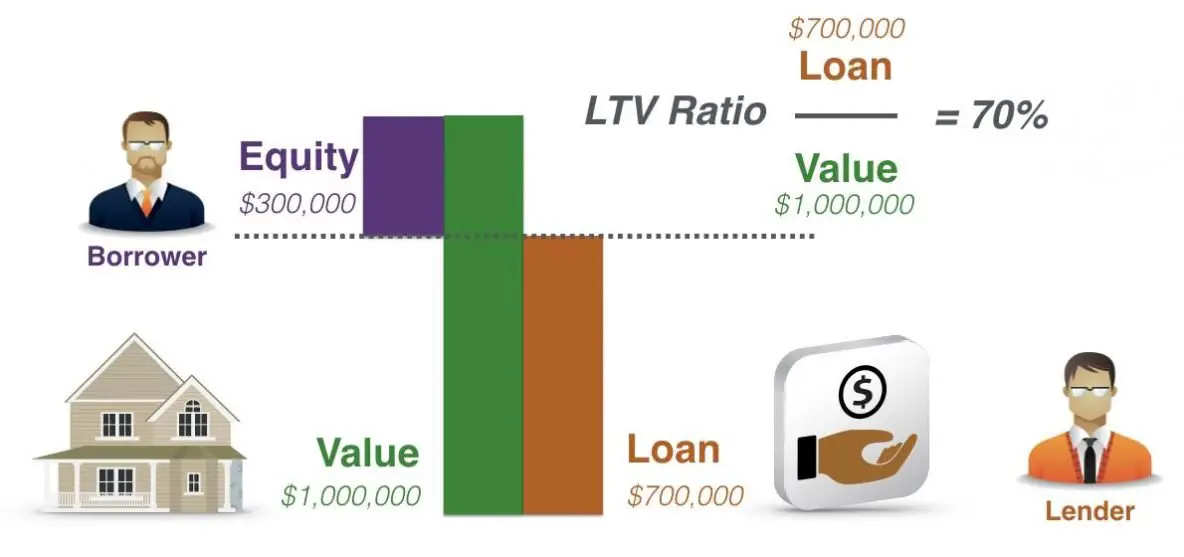
- Come in with a larger down payment if its a home purchase loan
- Ask for gift funds to increase your down payment
- Or break your mortgage up into two separate loans
- Make extra payments or a lump sum payment for a refinance to get the LTV down before you apply
- Or simply wait for natural amortization and home price appreciation to lower your LTV over time
If were talking about a home purchase, simply bring in more down payment money and the LTV will be lower. Easier said than done, sure, but possible for some.
Perhaps someone will gift you the money or act as a co-borrower?
Alternatively, you can look into breaking up your financing into two loans, with both a first and second mortgage.
If its a mortgage refinance, simply pay down the mortgage balance a bit more before you apply, whether on schedule or by making extra mortgage payments.
This can be especially helpful if youre super close to a certain LTV threshold, or just above the conforming loan limit.
Speaking of, pay close attention to your LTV if its just above 80% or some other meaningful tier, think about adjusting your loan amount down .
Lastly, theres another way existing homeowners can get their LTV down and it requires no effort whatsoever.
You dont have to do anything except sit back and watch your property value increase over time, thereby lowering your LTV in the process. Of course, the opposite can happen too if home values drop!
Don’t Miss: Can You Get A Reverse Mortgage On A Manufactured Home
Whats Behind The Numbers In Our Loan
This calculator helps you unlock one of the prime factors that lenders consider when making a mortgage loan: The loan-to-value ratio. Sure, a lender is going to determine your ability to repay including your , payment history and all the rest. But most likely, the first thing they look at is the amount of the loan youre requesting compared to the market value of the property.
An LTV of 80% or lower is most lenders sweet spot. They really like making loans with that amount of LTV cushion, though these days most lenders will write loans with LTVs as high as 97%.
Lets see how your LTV shakes out.
Make Regular Mortgage Payments
Making on-time mortgage payments will lower your principal balance and build your equity. It can be helpful to think of the ratio as a bookshelf, where the top shelf is the loan amount and the bottom shelf is the property value.
Any sturdy bookshelf will be bottom-heavy , with the heaviest books on the bottom and will want to keep the top shelf light. The more you pay off your loan and lighten the top shelf, the sturdier the bookshelf, and the more reliable you look to lenders.
At some point, youll have paid off enough of your loan to reach an 80% LTV ratio, meeting the 20% down payment requirement. This means you no longer need to pay private mortgage insurance, saving you hundreds of dollars per year.
Don’t Miss: Chase Recast
Definition And Example Of Loan
A loan-to-value ratio tells you how much of a property you truly own compared to how much you owe on the loan you took out to purchase it. Lenders use LTVs to determine how risky a loan is and whether they’ll approve or deny it. It can also determine whether mortgage insurance will be required.
- Acronym: LTV ratio
For example, if you buy a home that appraises for $200,000 and make a down payment of $20,000, you are borrowing $180,000 from the bank. The loan-to-value ratio on your mortgage would then be 90%.
The ratio is used for several types of loans, including home and auto loans, and for both purchases and refinances.
LTVs are part of a bigger picture that includes:
- Your credit score
- Your income available to make monthly payments
- The condition and quality of the asset youre buying
It’s easier to get higher LTV loans with good credit. In addition to your credit, one of the most important things lenders look at is your debt-to-income ratio, your debt payments divided by your income. This is a quick way for them to figure out how affordable any new loan will be for you. Can you comfortably take on those extra monthly payments, or are you getting in over your head?
Start With A Baseline Calculation
You can figure out how much equity you have in your home by subtracting the amount you owe on all loans secured by your house from its appraised value. This includes your primary mortgage as well as any home equity loans or unpaid balances on home equity lines of credit. In a typical example, homeowner Caroline owes $140,000 on a mortgage for her home, which was recently appraised at $400,000.
Also Check: Reverse Mortgage On Condo
Why You Can Trust Bankrate
Founded in 1976, Bankrate has a long track record of helping people make smart financial choices. Weve maintained this reputation for over four decades by demystifying the financial decision-making process and giving people confidence in which actions to take next.
Bankrate follows a strict editorial policy, so you can trust that were putting your interests first. All of our content is authored by highly qualified professionals and edited by subject matter experts, who ensure everything we publish is objective, accurate and trustworthy.
Our mortgage reporters and editors focus on the points consumers care about most the latest rates, the best lenders, navigating the homebuying process, refinancing your mortgage and more so you can feel confident when you make decisions as a homebuyer and a homeowner.
How To Calculate Ltv And Cltv
Calculating LTV has much to do with the down payment on your mortgage loan. Since your LTV is equal to the borrowed amount divided by the total home price, it’s the mirror opposite of the down payment. For instance, a $200,000 home bought with a down payment of 20% requires a mortgage loan of $160,000. Dividing that loan amount by the value gives us a LTV ratio of 80% the portion of your home value not covered by the 20% down payment.
Calculating LTV
| Loan balance divided by value = LTV | 80% |
You can figure out the combined loan to value ratio in a similar way. According to Fannie Mae’s guidelines on CLTV calculation for conventional mortgages, you must add the loan amount of your first mortgage to the amounts you have outstanding in your secondary mortgages, home equity loans and home equity lines of credit . For HELOCs, the CLTV takes into account the amount you have drawn so far on the line of credit. Once you add these numbers, you must divide the total by the lesser of two values: either the sales price of your home or its appraised value.
Calculating CLTV
| Sum of loans divided by value = CLTV | 82.5% |
As an example, consider our $200,000 home. Instead of a single mortgage of $160,000, we have a first mortgage of $90,000, a secondary mortgage of $70,000 and a HELOC that we’ve used to access $5,000 so far. Since the same home is being used to guarantee all three, we add the outstanding balances together and divide by $200,000 for a CLTV ratio of 82.5%.
Don’t Miss: Rocket Mortgage Payment Options
What Is Ltv In Mortgage Loan
Asked by: Clifford Beer V
The loan-to-value ratio is a measure comparing the amount of your mortgage with the appraised value of the property. The higher your down payment, the lower your LTV ratio. Mortgage lenders may use the LTV in deciding whether to lend to you and to determine if they will require private mortgage insurance.
loan to value ratioLTV ratio of 80% or lessloan-to-value ratio38 related questions found
How Ltv Is Used By Lenders

A LTV ratio is only one factor in determining eligibility for securing a mortgage, a home-equity loan, or a line of credit. However, it can play a substantial role in the interest rate that a borrower is able to secure.
Most lenders offer mortgage and home-equity applicants the lowest possible interest rate when their LTV ratio is at or below 80%. A higher LTV ratio does not exclude borrowers from being approved for a mortgage, although the interest on the loan may rise as the LTV ratio increases. For example, a borrower with an LTV ratio of 95% may be approved for a mortgage. However, their interest rate may be a full percentage point higher than the interest rate given to a borrower with an LTV ratio of 75%.
If the LTV ratio is higher than 80%, a borrower may be required to purchase private mortgage insurance . This can add anywhere from 0.5% to 1% to the total amount of the loan on an annual basis. For example, PMI with a rate of 1% on a $100,000 loan would add an additional $1,000 to the total amount paid per year . PMI payments are required until the LTV ratio is 80% or lower. The LTV ratio will decrease as you pay down your loan and as the value of your home increases over time.
In general, the lower the LTV ratio, the greater the chance that the loan will be approved and the lower the interest rate is likely to be. In addition, as a borrower, it’s less likely that you will be required to purchase private mortgage insurance .
Also Check: Reverse Mortgage For Condominiums
How To Calculate Your Home Equity And Why It Matters
As prices rise or fall in your area, your home equity also shifts. Hereâs a quick guide for figuring out how much you have, plus tips to potentially increase it.
WEâVE ALL DONE IT â that mental calculation where you try to figure out how much youâd clear if you were to sell your house and pay off your mortgage. But it can be more than just an idle exercise. Even if you never sell your home, the equity you have can help you pursue important personal goals. So understanding how to calculate your equity â and how banks view it â is critical, especially if you want to borrow money against that equity to pay for a home improvement project, cover emergency expenses or help pay for your childâs college tuition, for example. In fact, your homeâs equity also could affect whether you need to pay private mortgage insurance and could determine which financing options may be available to you.
Loan To Value Analysis
Loan to value is an important metric that categorizes borrowers. Though it is not the only metric that determines high-risk borrowers, it indicates how risky a loan is, and how the borrower will be motivated to settle the loan. It also determines how much borrowing will cost the borrower. The higher the loan to value ratio, the more expensive the loan.
Key factors that affect the loan to value ratio is the equity contribution of the borrower, the selling price and the appraised value. If the appraised value is high, that means a large denominator and hence a lower loan to value ratio. It can also be reduced by increasing the equity contribution of the borrower and reducing the selling price.
A major advantage of loan to value is that it gives a lender a measure of the level of exposure to risk he will have in granting a loan. The limitation of loan to value is that it considers only the primary mortgage that the owner owes, and not including other obligations like a second mortgage. A combined loan to value is more comprehensive in determining the likelihood of a borrower settling the loan.
Also Check: Does Getting Pre Approved Hurt Your Credit
What About Combined Ltv
If you already have a mortgage and want to apply for a second one, your lender will evaluate the combined LTV ratio, which factors in all of the loan balances on the property the outstanding balance on the first mortgage, and now the second mortgage.
Lets say you have an outstanding balance of $250,000 on a home that is appraised at $500,000, and you want to borrow $30,000 in a home equity line of credit to pay for a kitchen renovation. Heres a simple breakdown of the combined LTV ratio:
$280,000 / $500,000 = 56 percent CLTV
If you have a HELOC and want to apply for another loan, your lender may look at a similar formula called the home equity combined LTV ratio. This figure represents the total amount of the HELOC against the value of your home, not just what youve drawn from the line of credit.
Why Does Your Loan
Your loan-to-value ratio is important because it affects your monthly payment, down payment amount and closing costs.
The table below shows the differences between a 95% LTV ratio and an 80% LTV ratio on a 30-year, fixed-rate conventional purchase loan for a $250,000 home. It also assumes closing costs are 2% of the loan amount and the interest rate is 3.75%.
| LTV ratio | |
|---|---|
| $1,309.56** | $4,000 |
*Assumes $3,125 annual property taxes, $875 annual homeowners insurance, $123.70 per month mortgage insurance and $50 monthly HOA fees**Assumes $3,125 annual property taxes, $875 annual homeowners insurance and $50 monthly HOA fees
With a high-LTV ratio loan:
- Youll have a lower down payment, which leaves more cash in the bank.
- Youll have a higher monthly mortgage payment.
- You may have a harder time qualifying for a loan because of the higher payment.
- Your closing costs are higher due to a higher loan amount.
- You may end up losing money if you need to sell sooner than expected.
- You may need to pay monthly mortgage insurance premiums.
When it comes to a low-LTV ratio:
- Youll have a higher down payment, leaving you with less cash in the bank.
- Youll pocket more money when you sell because youll have more upfront equity.
- You may get a lower interest rate.
- Youll avoid paying mortgage insurance with 20% down.
- Youll have more home equity to tap if you need it in the future.
- Your closing costs may be lower because youre borrowing less.
Recommended Reading: How Much Is Mortgage On 1 Million
