Where Can You Find 10
You can find 10-year mortgages by looking at bank websites, online lenders, or through third-party comparison websites like Investopedia. Keep in mind that these rates are simply estimates and do not reflect individualized quotes youll receive after submitting an application form with your personal details.
Who Should Get An Arm
Im a big believer in an adjustable rate mortgage over a 30-year fixed rate mortgage. We are in a permanently lower interest rate environment thanks to technological efficiency, policy efficiency, and greater knowledge of economic cycles.
Further, given the average homeowner lives in their house for nine years, theres no need to get an ARM longer than a 10/1. Longer fixed duration loans cost more money because the yield curve is generally upward sloping.
Finally, it is not recommended to spend 30 years to pay off your house. If you do, youll end up paying an enormous amount of interest on your home. Try to pay off your house within 15 years. Youll save money and feel great knowing you are mortgage debt free.
Shop around for a lower mortgage rate:Check the latest mortgage rates online. Youll get real quotes from pre-vetted, qualified lenders in under three minutes. The more free mortgage rate quotes you can get, the better. This way, you feel confident knowing youre getting the lowest rate for your situation. Further, you can make lenders compete for your business.
As a multi-property homeowner since 2003, I truly believe a 10/1 ARM is one of the best types of mortgages to get. Take advantage of low mortgage rates!
Conforming Vs Nonconforming Arm Loans
Beyond the loan term, youll encounter conforming loans and nonconforming loans as you explore your ARM options.
Conforming loans are mortgages that meet specific guidelines that allow them to be sold to Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac. Lenders can sell mortgages that they originate to these government-sponsored entities for repackaging on the secondary mortgage market if the mortgages conform to the funding criteria of Fannie and Freddie and the Federal Housing Finance Agencys dollar limits.
If a loan doesnt meet these specific guidelines, it will fall into the nonconforming category. But beware of the potential pitfalls before jumping into a nonconforming loan.
Although good reasons exist why borrowers may need a nonconforming mortgage, and most originators of these loans are reputable, many are not. If youre considering a nonconforming ARM, be sure to read the fine print about rate resets very carefully so you understand how they work.
Its important to note that FHA and VA ARMs are considered nonconforming according to the rules of Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac, but they have the full backing of the U.S. government which might make some home buyers feel more comfortable choosing one of these loans.
Read Also: How Much Would A Mortgage Be On 130 000
Higher Rates Aren’t Necessarily A Bad Thing
Things don’t happen in a vacuum. The 10-year Treasury yield is a reflection of inflation and economic growth predictions.
If yields and mortgage rates are rising, it probably means that inflation is elevated because demand is increasing. So even if you have a higher mortgage rate, the value of your home will most likely be higher due to strong demand.
Given that the cost of homeownership is largely fixed, real estate is not only an inflation hedge, but it is also an inflation play. In an extreme circumstance where there is hyperinflation, it is wise to own real assets such as real estate instead of cash, which is rapidly losing its purchasing power.
How Do Fixed Rates Compare To A 5/1 Arm Loan
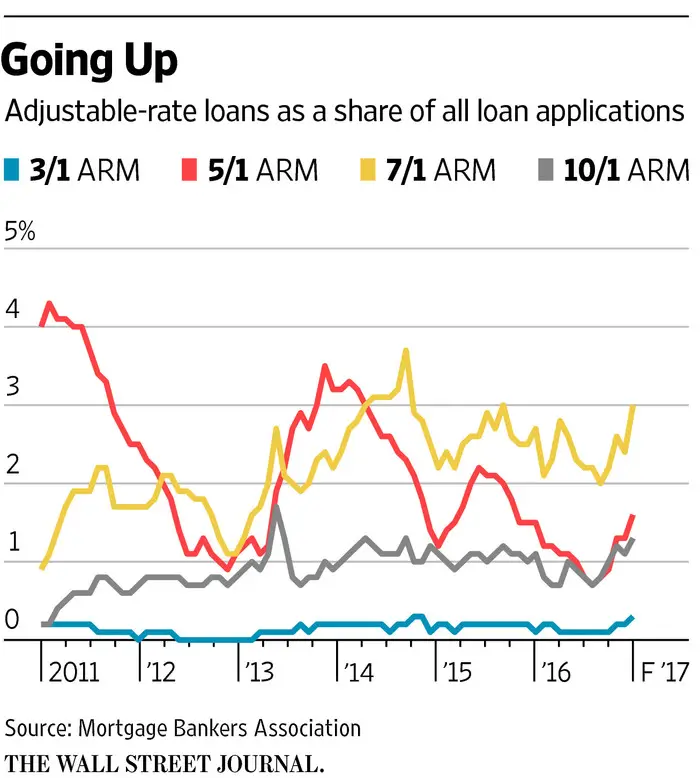
Most homeowners prefer the stability of a low, 30-year fixed-rate mortgage payment for the life of their loan. However, if current 30-year mortgage rates are too high, a 5/1 ARM rate makes sense especially if youre planning to relocate within five years and want to stash the savings from a five-year ARM payment into a moving expense account.
Below is a side-by-side look at the features of a fixed-rate mortgage versus a 5/1 ARM.
| Features of a 5/1 ARM | Features of a fixed-rate mortgage |
|---|---|
| Payment is typically lower than fixed-rate loans for the first five years | Payment is higher than 5/1 ARMs during the temporary fixed-rate period |
| Variable rate could increase after the teaser period ends | Rate is fixed for the life of the loan |
Recommended Reading: What Is The Shortest Mortgage Term Available
How A 10/1 Arm Works
ARMs adjust over time, resulting in a lower or higher monthly payment, depending on how rates are fluctuating. Your payment changes to ensure that your mortgage is paid off on time.
With a 10/1 ARM, your mortgage rate will begin to change after the fixed-rate period of 10 years.
There are often caps on how much a rate can adjust upward, which might save you from unmanageable monthly payments. Heres a closer look at how 10/1 ARMs work:
How Does A 10/1 Arm Refinance Loan Work
A 10/1 ARM loan is a cross between a fixed-rate loan and a variable-rate loan. After an initial 10-year period, the fixed rate converts to a variable rate. It remains variable for the remaining life of the loan, adjusting every year in line with an index rate. This index rate fluctuates with market conditions. Your monthly mortgage payment could increase substantially if the index rate increases substantially. If the index rate declines, then your monthly mortgage payment could decrease. Some 10/1 ARMs set limits on how high or low the rate may change.
Recommended Reading: How To Make A 30 Year Mortgage A 15
How To Compute The Monthly Payment Of An 10/1 Arm Loan
Follow the below steps to compute the monthly payment of a 10/1 ARM.
Compute the periodic equivalent rate by dividing the annual rate by 12.
Determine the number of periods by multiplying 12 with the number of years.
Use the below formula to compute the monthly payment fixed for the first ten years:
Payment = t) / t – 1)
Mortgage Rates For Sept 30 202: Rates Increase
A handful of notable mortgage rates ticked up this week. If you’re shopping for a home loan, see how your payments might be affected by inflation.
A couple of principal mortgage rates climbed up over the last week. The average 15-year fixed and 30-year fixed mortgage rates both inched upward. For variable rates, the 5/1 adjustable-rate mortgage also climbed higher.
Mortgage rates have been increasing consistently since the start of 2022, following in the wake of a series of interest hikes by the Federal Reserve. Interest rates are dynamic and unpredictable — at least on a daily or weekly basis — and they respond to a wide variety of economic factors. But the Fed’s actions, designed to mitigate the high rate of inflation, are having an unmistakable impact on mortgage rates.
If you’re looking to buy a home, trying to time the market may not play to your favor. If inflation continues to increase and rates continue to climb, it will likely translate to higher interest rates — and steeper monthly mortgage payments. As such, you may have better luck locking in a lower mortgage interest rate sooner rather than later. No matter when you decide to shop for a home, it’s always a good idea to seek out multiple lenders to compare rates and fees to find the best mortgage for your specific situation.
You May Like: What Is A Cash Out Refinance Mortgage
How Adjustable Rate Mortgages Are Calculated
The method for calculating interest rates on ARMs is based on a simple mathematical formula: index rate + margin = interest rate.
The index rate typically is based on one of three indexes: the London Interbank Offered Rate the one-year Treasury Bill or the Cost of Funds Index . Some lenders have their own cost of funds index so its important that you ask what index is being used and where it is published so you can keep track of it.
Your lender chooses which index to base your rate on when you apply for the loan, but the LIBOR is the most popular index used.
Your lender also determines the margin you will pay, which is the number of percentage points added to index. The margin percentage varies from one lender to the next and should be a focal point of your research when applying for an ARM. That margin should be constant throughout the life of your loan.
In the spring of 2018, the LIBOR index was 2.66%. The common margin rate was around 2.75%. Using the formula above index rate + margin = an interest rate of 5.41%.
Pros And Cons Of An Arm
With a 10/1 ARM, you know exactly what your interest rate will be for the first 10 years. After that, your interest rate, and therefore your monthly payment, could go up or down.
Weve been in a declining or low interest rate environment for over 40 years. Rates started to go up in 2022, but notice how much lower they still are compared to the 80s and 90s. Chances are still good that your payment wont go up too much once the 10-year fixed period is up.
Not only may interest rates be similar 10 years from now, your principal balance will have absolutely declined by at least 10%.
With a lower principal balance to pay off upon interest rate adjustment, even if interest rates increased a lot, it would be offset by the lower balance.
10/1 ARM Example
Lets say you are purchasing a $500,000 house and putting down 20 percent. You could borrow $400,000 at a 4.5 percent interest rate at a monthly payment of $2,027.
Alternatively, you could take out a 10/1 ARM for the $400,000 loan and borrow at a 3.5 percent interest rate. Your payment would go down to $1,796 a month, thereby improving your cash flow by $231 a month.
After 10 years when its time for your ARM to adjust, your principal amount will decline to roughly $360,000. Even if your mortgage rate adjusts to 4 percent from 3.5 percent, youre still paying roughly the same amount in monthly mortgage payments.
You May Like: Why Do You Need Mortgage Insurance
Which Loan Is Right For You
When choosing a mortgage, you need to consider a wide range of personal factors and balance them with the economic realities of an ever-changing marketplace. Individuals personal finances often experience periods of advance and decline, interest rates rise and fall, and the strength of the economy waxes and wanes. To put your loan selection into the context of these factors, consider the following questions:
- How large a mortgage payment can you afford today?
- Could you still afford an ARM if interest rates rise?
- How long do you intend to live on the property?
- In what direction are interest rates heading, and do you anticipate that trend to continue?
If you are considering an ARM, you should run the numbers to determine the worst-case scenario. If you can still afford it if the mortgage resets to the maximum cap in the future, an ARM will save you money every month. Ideally, you should use the savings compared to a fixed-rate mortgage to make extra principal payments each month, so that the total loan is smaller when the reset occurs, further lowering costs.
If interest rates are high and expected to fall, an ARM will ensure that you get to take advantage of the drop, as youre not locked into a particular rate. If interest rates are climbing or a steady, predictable payment is important to you, a fixed-rate mortgage may be the way to go.
Interest Rate Errors And Overcharges
In September 1991, the Government Accountability Office released a study of Adjustable Rate Mortgages in the United States which found between 20% and 25% of the ARM loans out of the estimated 12 million at the time contained Interest Rate Errors. A former federal mortgage banking auditor estimated these mistakes created at least US$10 billion in net overcharges to American home-owners. Such errors occurred when the related mortgage servicer selected the incorrect index date, used an incorrect margin, or ignored interest rate change caps.
In July 1994, Consumer Loan Advocates, a non-profit mortgage auditing firm announced that as many as 18% of Adjustable Rate Mortgages have errors costing the borrower more than $5,000 in interest overcharges.
In December 1995, a government study concluded that 50â60% of all Adjustable Rate Mortgages in the United States contain an error regarding the variable interest rate charged to the homeowner. The study estimated the total amount of interest overcharged to borrowers was in excess of $8 billion. Inadequate computer programs, incorrect completion of documents and calculation errors were cited as the major causes of interest rate overcharges. No other government studies have been conducted into ARM interest overcharges.
Also Check: How To Work For A Mortgage Company
Wrapping It Up Is A 10/1 Arm Loan Right For Me
If you plan to sell or refinance your home within the first 10 years you own it, a 10/1 ARM loan might be the perfect choice for you. If youre able to make extra payments or can handle variable payments later on, a 10/1 ARM loan can save you major money, even if you stay in your home longer than 10 years.
Keep in mind that this loan comes with more risk-tolerance requirements than a 15- or 30-year fixed-rate mortgage. If you are currently shopping for mortgages, remember that lenders are looking at your credit history and financial health. Great credit can help you get the best rates regardless of which mortgage you choose.
How Does A 5/1 Arm Work
During the initial fixed-rate period, the rate is typically lower. After that, the rate can change based on five factors:
- The initial adjustment cap. Once the fixed rate expires, the initial adjustment cap limits how much the interest rate can rise. The initial adjustment cap is generally 2% or 5%, meaning the new rate cant rise by more than two or five percentage points.
- The adjustment period. Rate changes to an ARM mortgage are based on the adjustment period. For example, a 5/1 ARM will adjust every year after the five-year teaser-rate period ends. Lenders may offer adjustment periods ranging from monthly to every five years.
- The index. An index is a benchmark variable rate that fluctuates based on market and economic conditions. The margin is added to your index to determine your rate with each adjustment period, and lenders should provide information to illustrate how the chosen index has changed over time.
- The margin. A margin is a fixed number set by the lender and added to the index to determine your rate when it adjusts.
- The lifetime cap. Many ARMs have a 5% lifetime cap, which means your rate can never be more than five percentage points higher than the initial rate.
THINGS YOU SHOULD KNOW
Don’t Miss: What Is The Average 15 Year Fixed Mortgage Rate
How To Qualify For An Arm Loan
As with all mortgages, ARM loans come with several requirements. You should be prepared to prove your income with W-2s, pay stubs and other documentation. Your income level will help the lender determine how large of a mortgage payment you qualify for.
Additionally, youll need a relatively good credit score to qualify. For example, most loans will require at least a 620 FICO® Score.
Arms Future Monthly Payment Challenge
As you might know, its pretty easy to get a rough idea of what your payments will look like over the course of a mortgage with a fixed APR. You just find an online mortgage payment calculator and run the numbers. But these mortgage calculators dont do ARMs. Even Alliant Credit Union, a company with positive SuperMoney reviews that offers a 10/6 ARM, links an article on its adjustable-rate product to a mortgage calculator configured for fixed rates.
Your future monthly mortgage payment: Nothing to worry about?
Now, Alliant points out that few borrowers keep a mortgage more than 10 years and a majority of homebuyers move to a new home within 8 years. So, Alliant reasons, why worry about what might happen 10 years from now? Does Alliant have a point?
Perhaps. Still, you cannot say for certain that interest rates 10 years from now will not be going up. You also cant say for certain that your credit will be as good then as it is today. What if interest rates start climbing and you cant qualify for a refinance with appealing rates? What if home sales are also sluggish and you cant get a satisfactory price selling?
In personal finance, ignorance is not bliss
Before you commit to an ARM, you should try to get some feel for what might happen if you have to stay with it till you get your home paid off. Hoping for the best will never hurt you. Preparing only for the best could hurt you a great deal.
Also Check: How Much Money Can I Get Preapproved For A Mortgage
When Should You Consider A 10
A 10-year ARM makes sense if you plan to refinance your mortgage or sell your house before the introductory rate expires or if you expect the value of your house to rise quickly. If you choose an ARM, youll likely be able to qualify for a larger loan because of the low introductory rate. But be careful, your interest rate and monthly payment will increase after the 10-year introductory period, and can climb substantially depending on the terms of your specific loan.
Do You Pay Principal On An Arm
ARMs are fully amortized home loans. Like fixed-rate loans for property, ARMs come with a payment schedule that will zero them out over the life of the loan. This means you pay both principal and interest every time you make a payment. The big difference between ARM payment schedules and fixed-rate schedules is that future scheduled payments can change every time the rate adjusts.
View Article Sources
Also Check: How Do You Calculate Self Employed Income For A Mortgage