A Changing Rate Environment In 2022 Could Benefit Active Mbs Investors
Boston 2021 is a year most agency Mortgage-Backed Securities investors will be happy to have in the rearview mirror. The agency MBS market underperformed nearly all other U.S. fixed-income sectors in 2021 and suffered only its second negative year over the past 25 years, as measured by the Bloomberg US Mortgage Backed Securities Index. Both negative years were actually the byproduct of the same event, eight years apart tapering of the Feds quantitative easing programs. While most agency MBS investors expected the Fed to taper its MBS purchases before 2021 was over, the real surprise of 2021 was the seemingly never-ending amount of supply, which hit the market month after month.
| CFA, Director, Mortgage-Backed Securities – Eaton Vance Management |
All investing involves risk, including the risk of loss.
Definitions
ICE BofA U.S. MBS Index tracks the performance of U.S. dollar-denominated investment-grade asset-backed securities publicly issued in the U.S. domestic market.
Risk Considerations
Investing entails risks and there can be no assurance that any strategy will achieve profits or avoid incurring losses.
Important Information
Date-of Data: December 27, 2021
There is no guarantee that any investment strategy will work under all market conditions, and each investor should evaluate their ability to invest for the long-term, especially during periods of downturn in the market.
For important information about the investment managers, please refer to Form ADV Part 2.
EMEA:
Examples Of More Common Types Of Cmo Classes
Sequential Class is the most basic CMO structure. Each class receives regular monthly interest payments. Principal is paid to only one class at a time until it is fully paid off. Once the first class is retired, the principal is then redirected to the next class until it is paid off, and so on. The classes are paid off based on their corresponding average maturities, which may be 2-3 years, 5-7 years, 10-12 years, etc. This type of structure may help reduce prepayment variability.
Planned Amortization Class offers a fixed principal payment schedule. This is done by redirecting cash flow irregularities caused by faster-than-expected principal repayments away from the PAC class and toward another class referred to as a support class.
In other words, two or more classes are active at the same time. When repayment of principal is less than scheduled, principal is paid to the PAC class while principal to the support class is suspended. With a PAC class, the yield, average life, principal window and principal return lockout periods estimated at the time the deal is structured are more likely to remain stable over the life of the security.
What Is An Asset
An asset-backed security is a type of financial investment that is collateralized by an underlying pool of assetsusually ones that generate a cash flow from debt, such as loans, leases, credit card balances, or receivables. It takes the form of a bond or note, paying income at a fixed rate for a set amount of time, until maturity.
For income-oriented investors, ABSs can be an alternative to other debt instruments, like corporate bonds or bond funds. For issuers, ABSs allow them to raise cash which can be used for lending or other investment purposes.
Recommended Reading: How To Qualify For A Va Loan Mortgage
Are Mortgage Backed Securities A Good Investment
Mortgage-backed securities can play a part in an investment portfolio however, individual investors may have difficulty assessing the creditworthiness of the security issuer. This complexity adds additional risk that should be discussed with a professional financial advisor to see if an MBS fund is right for your financial circumstances.
The Role Of Mbs In The 2008 Financial Crisis

Low-quality mortgage-backed securities were among the factors that led to the financial crisis of 2008. Although the federal government regulated the financial institutions that created MBS, there were no laws to directly govern MBS themselves.
The lack of regulation meant that banks could get their money right away by selling mortgages immediately after making the loans, but investors in MBS were essentially not protected at all. If the borrowers of mortgage loans defaulted, there was no sure way to compensate MBS investors.
The market attracted all types of mortgage lenders, including non-bank financial institutions. Traditional lenders were forced to lower their credit standards to compete for home loan business.
At the same time, the U.S. government was pressuring lending institutions to extend mortgage financing to higher credit risk borrowers. This led to the creation of massive amounts of mortgages with a high risk of default. Many borrowers simply got into mortgages that they eventually could not afford.
Recommended Reading: How To Become A Mortgage Processor In Florida
How A Residential Mortgage
A residential mortgage-backed security is constructed by one of two sources: a government agency such as the Federal National Mortgage Association and the Federal Home Loan Mortgage Corporation , or by a non-agency investment-banking firm. First these entities sell or control a large number of residential loans. Next they package a large number of them together into a single pool of loans. Finally these entities essentially sell bonds backed by this pool of loans.
The payments on these loans flow through to the investors who bought into this pool, and the interest rates they receive are better than typical U.S. government-backed bonds. The issuing institutions keep a fee for the management of the pool, and the risks of default on these mortgages are shared by both the issuing entities and the investors. Because each of these loans is a small part of the larger, collected pool of loans, the default of any one of these loans has less impact on the investors than if they were to invest in any one of these loans individually.
The Following Terms Will Help You Further Understand A Bonds Psa Analysis:
The Average Life of a mortgage bond is the average time that each principal dollar in the pool is expected to be outstanding, based on an estimated PSA. If the actual prepayment speed is faster or slower than estimated, the average life will be shorter orlonger. It is a general practice to quote average life rather than the stated maturity date when evaluating mortgage-backed securities.
Yield-to-Average Life is a standard measure of return used to compare MBS to other fixed income alternatives with similar characteristics. However, average life is only an estimate and largelydepends on the accuracy of prepayment speed assumptions.
1st principal is the expected first principal payment based on the PSA
Last principal is the expected final principal payment based on the PSA
1 month actual is the actual PSA for the prior month
Three month, six month, 12 month, Lifetime Avg is the historical average PSA.
Yield and average life consider prepayment assumptions that may or may not be met. Changes in payments may significantly affect yield and average life.
Recommended Reading: How To Pick The Best Mortgage Lender
What’s The Relationship Between Mbs And A Bank
Essentially, the mortgage-backed security turns the bank into an intermediary between the homebuyer and the investment industry. A bank can grant mortgages to its customers and then sell them at a discount for inclusion in an MBS. The bank records the sale as a plus on its balance sheet and loses nothing if the homebuyer defaults sometime down the road.
This process works for all concerned as long as everyone does what they’re supposed to do. That is, the bank keeps to reasonable standards for granting mortgages the homeowner keeps paying on time, and the credit rating agencies that review MBS perform due diligence.
It’s Known That Mortgage Loans Were Instrumental To The Financial Crash Of 2008 And Because Of That Many Investors Swore Off Mortgage
It’s known that mortgage loans were instrumental to the financial crash of 2008, and because of that many investors swore off mortgage-backed securities. But the and is profitable again. If you have some experience investing in mortgage-backed securities and you decide to get back into it, then we would advise you proceed with caution and first gather as much information as you can about the current state of the market. But if you are a new investor, then read on to learn how to get started to invest in RMBS.
What role did banks and MBS play in the crash of 2008?
Prior to 2007, the real estate market wasn’t exactly booming. The dotcom bust gave rise to many companies that weren’t exactly performing, but whom venture capitalists and the general public poured money into. In 2001, central banks tried to stimulate cash flow by cutting interest rates which made hungry investors take on riskier ventures.
This spilled into the real estate market. Lenders started giving out loans to people with bad credit and low income and banks started removing many restrictions to lending, restrictions that protected from bad debt. The banks lent to people without down payments and sometimes even fully funded homes because they could easily sell the loans to investors. This gave rise to a housing bubble, and when it burst, lots of people realized they could not afford their loans and defaulted.
Freddie Mac and Fannie Mae
Mortgage REITs
Mutual Funds
Recommended Reading: How Much Will I Be Preapproved For A Mortgage
How Can You Invest In An Mbs
You can buy individual MBSs through a broker, but this option is limited to those with the time and knowledge to conduct their own fundamental research. This research should take into account the average age, geographic location, and credit profile of the underlying mortgages.
Many people who own a broad-based bond mutual fund or exchange-traded fund have some exposure to this sector since it is such a large portion of the market. It is heavily represented in diversified funds. You can also opt for funds that are dedicated solely to MBSs. Some of the ETFs that invest in this space are:
- Barclays Agency Bond Fund
- iShares Barclays MBS Fixed-Rate Bond Fund
- Mortgage-Backed Securities ETF
- iShares Barclays GNMA Bond Fund
- SPDR Barclays Capital Mortgage Backed Bond ETF
Investing In Residential Mortgage
Investing in a residential-mortgage backed security can expose the investor to prepayment risk and . Prepayment risk is the risk that the mortgage holder will pay back the mortgage before its maturity date, which reduces the amount of interest the investor would have otherwise received. Prepayment, in this sense, is a payment in excess of the scheduled principal payment. This situation may arise if the current market interest rate falls below the interest rate of the mortgage, since the homeowner is more likely to refinance the mortgage. Credit risk for RMBS investors arises when the borrower stops making payments on his mortgage
Residential mortgage-backed securities are utilized by financial institutions like insurance companies because of their cash flow characteristics and their relatively long lives, which can offset long-term liabilities taken on by insurance companies. Moreover, buyers of residential mortgage-backed securities often have input into how they are constructed, so they can be uniquely tailored to offset a liability or to fit other investor preferences for risk, return and timing of cash flows, for example.
Read Also: What Is A Mortgage Modification Agreement
Mortgage Bonds And Mortgage
Lenders of mortgage bonds and loans, such as banks, do not usually retain the ownership of mortgages. Instead, they securitize the mortgages into financial products that can be sold in the secondary market. Such a type of financial product is known as a mortgage-backed security .
A special purpose vehicle the originator of the MBS gathers mortgages from a bank into a pool and sells small packages of the mortgages to investors. The originator gathers interest payments from the mortgage borrowers and then distributes the payments to the MBS investors. Hence, the default risk is transferred to the MBS investors.
The Role Of Government In Mbs
As a response to the Great Depression of the 1930s, the government established the Federal Housing Administration to help in the rehabilitation and construction of residential houses. The agency assisted in developing and standardizing the fixed-rate mortgage and popularizing its usage.
In 1938, the government created Fannie Mae, a government-sponsored agency, to buy the FHA-insured mortgages. Fannie Mae was later split into Fannie Mae and Ginnie Mae to support the FHA-insured mortgages, Veterans Administration, and Farmers Home Administration-insured mortgages.,
In 1970, the government created another agency, Freddie Mac to perform similar functions to those performed by Fannie Mae.
Freddie Mac and Fannie Mae both buy large numbers of mortgages to sell to investors. They also guarantee timely payments of principal and interest on these mortgage-backed securities. Even if the original borrowers fail to make timely payments, both institutions still make payments to their investors.
The government, however, does not guarantee Freddie Mac and Fannie Mae. If they default, the government is not obligated to come to their rescue. However, the federal government does provide a guarantee to Ginnie Mae. Unlike the other two agencies, Ginnie Mae does not purchase MBS. Thus, it comes with the lowest risk among the three agencies.
Also Check: Why Does My Mortgage Loan Keep Getting Transferred
What Is A Mortgage
A Mortgage-backed Security is a debt security that is collateralized by a mortgage or a collection of mortgages. An MBS is an asset-backed security that is traded on the secondary market, and that enables investors to profit from the mortgage business without the need to directly buy or sell home loans.
Mortgages are sold to institutions such as an investment bank or government institution, which then package it into an MBS that can be sold to individual investors. A mortgage contained in an MBS must have originated from an authorized financial institution.
When an investor buys a mortgage-backed security, he is essentially lending money to home buyers. In return, the investor gets the rights to the value of the mortgage, including interest and principal payments made by the borrower.
Selling the mortgages they hold enables banks to lend mortgages to their customers with less concern over whether the borrower will be able to repay the loan. The bank acts as the middleman between MBS investors and home buyers. Typical buyers of MBS include individual investors, corporations, and institutional investors.
Mbs And The Financial Crisis
Mortgage-backed securities played a central role in the financial crisis that began in 2007 and went on to wipe out trillions of dollars in wealth, bring down Lehman Brothers, and roil the world financial markets.
In retrospect, it seems inevitable that the rapid increase in home prices and the growing demand for MBS would encourage banks to lower their lending standards and drive consumers to jump into the market at any cost.
Also Check: Can A Second Mortgage Be Discharged In Chapter 7
How They Are Formed
Mortgage-backed securities are debt obligations purchased from banks, mortgage companies, credit unions, and other financial institutions and then assembled into pools by a governmental, quasi-governmental or private entity. These entities then sell the securities to investors. This process is illustrated below:
Mbs And Specialized Considerations
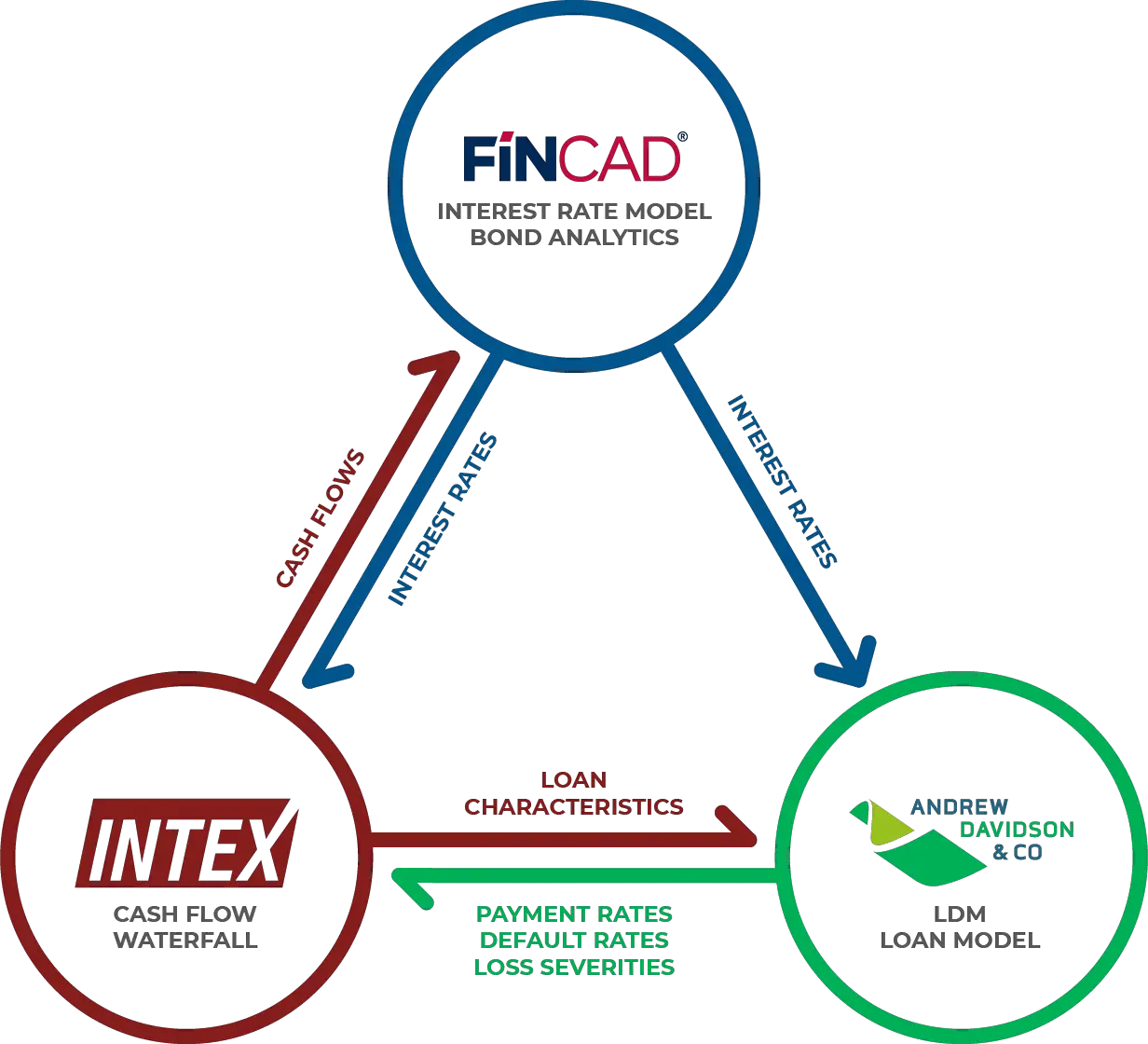
What we hear from our clients, is the largest challenge they have with MBS comes down to modeling. The fact is that MBS are a complex investment type, and thus require very specialized modeling considerations.
To get MBS modeling right, you need access to a highly flexible MBS analytics framework. Modeling MBS is an area where FINCAD F3 shines and offers unique advantages over other providers out there.
F3s MBS framework design is generic and flexible enough to support any kind of MBS analysis that you want to carry out. Using F3, you can identify the fundamental concepts in your analysis workflow. From there, you can use these concepts as building blocks that combine to form a complete MBS analytics system.
Another area that sets F3 apart is that it provides one consistent modeling framework to be used across all assets in your portfolio, including MBS. So, you are able to model, value and run risk on your entire portfolio of securities and derivativesand even build out custom reporting for all of it. This is an ability that no other MBS modeling solution provider has matched to date and one that has proven very advantageous for our clients.
Recommended Reading: What Is The Monthly Payment On A 75000 Mortgage
The Past Few Months Have Been Abysmal For Mortgage
This year has been especially tough for the mortgage market and housing in general. The press talks about a housing recession, builders have slowed home construction, mortgage origination volume has been cut in half, and the mortgage real estate investment trusts have been hammered by rising rates and underperforming portfolios.
As the year has worn on, the dividend yields on many mortgage REITs have reached levels where dividend cuts have occurred in the past. AGNC Investment recently reported earnings and gave some color on its thinking regarding the dividend, which now stands at about 17.7%.
Image source: Getty Images.
Does The Federal Reserve Buy Mortgage
The Federal Reserve had only an indirect impact on mortgage rates until 2008. Around this time, the Fed began buying MBSs directly in order to support the economy, help decrease mortgage interest rates and add liquidity to the market. This practice continued for over a decade, with the Fed amassing more than $2 trillion in MBS holdings. Recently, however, the Fed has made the decision to slowly exit the MBS market by halting its continual purchasing of bonds.
The purchase of these MBSs was helping keep mortgage rates low, which provided an economic boost because housing accounts for a fairly large share of money pumped into the economy. However, cheaper financing meant higher home prices something that is, at this point, actually detrimental. By halting its purchase of MBSs, the Fed hopes to combat inflation.
Recommended Reading: How To Figure Out What Mortgage You Qualify For