Does The Fed Control Mortgage Rates
No. Data from the past half century show that the federal funds rate and average mortgage rate across the land are almost never aligned and, in fact, usually differ significantly.
For example, the federal funds rate has rested between 0 percent and 0.25 percent since March 2020. The national average for 30-year mortgage rates, however, has mainly hovered above 3 percent during this time. The yield on a 10-year Treasury note is more closely aligned with mortgage rates but again, is rarely an exact match.
In reality, mortgage rates are impacted by many factors, from the appetite for risk lenders possess to the national rate of inflation to an applicants credit score and more.
What Are Interest Rates
Many of us hear about interest rates for all sorts of things. We have interest rates on our credit cards, student loans, car loans, mortgages, and savings accounts. But what are interest rates, and how do they work?
Interest rates are effectively fees that the bank charges or pays you for the lending of money. When you pay interest on a car note or a mortgage, youre paying the bank a small percentage of the loan amount for the privilege of borrowing their money. The interest you earn on savings accounts is payment from the bank for the privilege of using your money to finance other transactions.
What Does The Federal Reserve Do
The Federal Reserve does quite a lot for the country, but the institution is often characterized by its dual mandate to stabilize the price of goods and increase employment. According to the Fed, its core functions cover four key areas:
- Setting and supporting a monetary policy for the entire country
- Monitoring banks and regulating financial institutions to protect consumers and ensure monetary policies are being followed
- Minimizing risk to financial systems and fostering a stable banking environment
- Providing financial services to both the U.S. government and certain foreign institutions
Youve probably noticed that we didnt mention mortgage rates or interest rates at all. Thats because the Fed does not set interest rates. The lending industry weighs a wide variety of factors to set mortgage rates. But that doesnt mean the Fed is completely disengaged from this process. Its role is just a bit more indirect than you might initially think.
Read Also: How Much Mortgage Interest Can I Deduct
Why Is The Fed Raising Rates
The short answer: To get record-high inflation under control.
Americans have been slammed by double-point percentage increases on the prices of just about everything they need to survive: Food. Gas. Utilities.
Changing the target for the federal funds rate is one of the few tools the central bank can employ to stabilize an overheated economy and moderate demand for goods, which can reduce inflation.
For months, Powell and other Fed officials have been repeating over and over that the four-decade highs in U.S. inflation rates were making tighter monetary policy an absolute necessity. Its also become clear that the jobs market has almost entirely healed as the Covid-19 pandemic wanes, with the unemployment rate at 3.6%.
Congress has bestowed two jobs on the Fed: keep prices under control and promote full employment. It appears that the latter job is done, so the Fed is moving to tackle the former by tightening monetary policy.
Analysts expect the Fed to deliver two more hikes in 2022. The Fed has projected the median federal funds rate will reach 3.4% by the end of 2022.
Heres the big challenge: The Fed must raise rates to curb inflation, but it cant increase rates too high, or it could cause a recession. And some economists believe its getting increasingly difficult for the Fed to straddle this line and avoid a shrinking economy.
How The Fed Rate Hike Affects Home Buyers

High rates mean you pay more interest, which can reduce your buying power because you wont be able to borrow as much money. Thats because less money will be going to paying your principal and more money will be going to paying your interest.
For example, the monthly mortgage payment for a 30-year mortgage on a $200,000 loan at a 6% rate is $1,199. If the interest rate were 3%, you could buy a $285,000 home for the same monthly payment.
There could be a benefit for home buyers whove been dealing with high home prices and an extremely competitive market. Higher interest rates could help decrease the demand that is currently driving up prices. If youre a home buyer, keep an eye on the local market and consider locking your rate when youre ready to move forward.
Remember, too, that just because you qualify for a certain amount doesnt mean you should borrow the maximum. Take the time to work through how much house you can afford, including monthly payments. Work with your lender to get an estimate of what your monthly mortgage payment could be with different loan amounts and various interest rates.
Lock your low rate today!
Get approved before interest rates continue to rise.
You May Like: What Are Current Residential Mortgage Rates
How Does The Fed Rate Increase Affect Mortgages
At the end of April, the Bureau of Labor Statistics reported that the Consumer Price Index measured year-over-year inflation at 8.5%. The Consumer Price Index is a calculation that tracks how much the average cost of consumer items changes over time and is a widely used method of measuring inflation.
Like most consumers, youre probably concerned about the continued reports of increasing inflation, and likely feeling the brunt of these growing numbers. You can see the increase in overall price levels at the supermarket buying groceries, filling up on gas, or in your monthly energy bills.
The Federal Reserve, which is charged with navigating US financial policy, is working to address those concerns and stomp out this continued inflation. Raising the federal funds rate is a tried-and-true economic lever they can pull to help counteract inflation.
One concern is how inflation and increasing rates will affect bigger-ticket purchases, like cars or homes. If youre in the market to buy or sell a home, youre probably also concerned with how this is affecting mortgage rates and the housing market. In this post, we explain the most recent Fed rate increase that happened this month, how its affecting the real estate market, and the current outlook for the rest of the year.
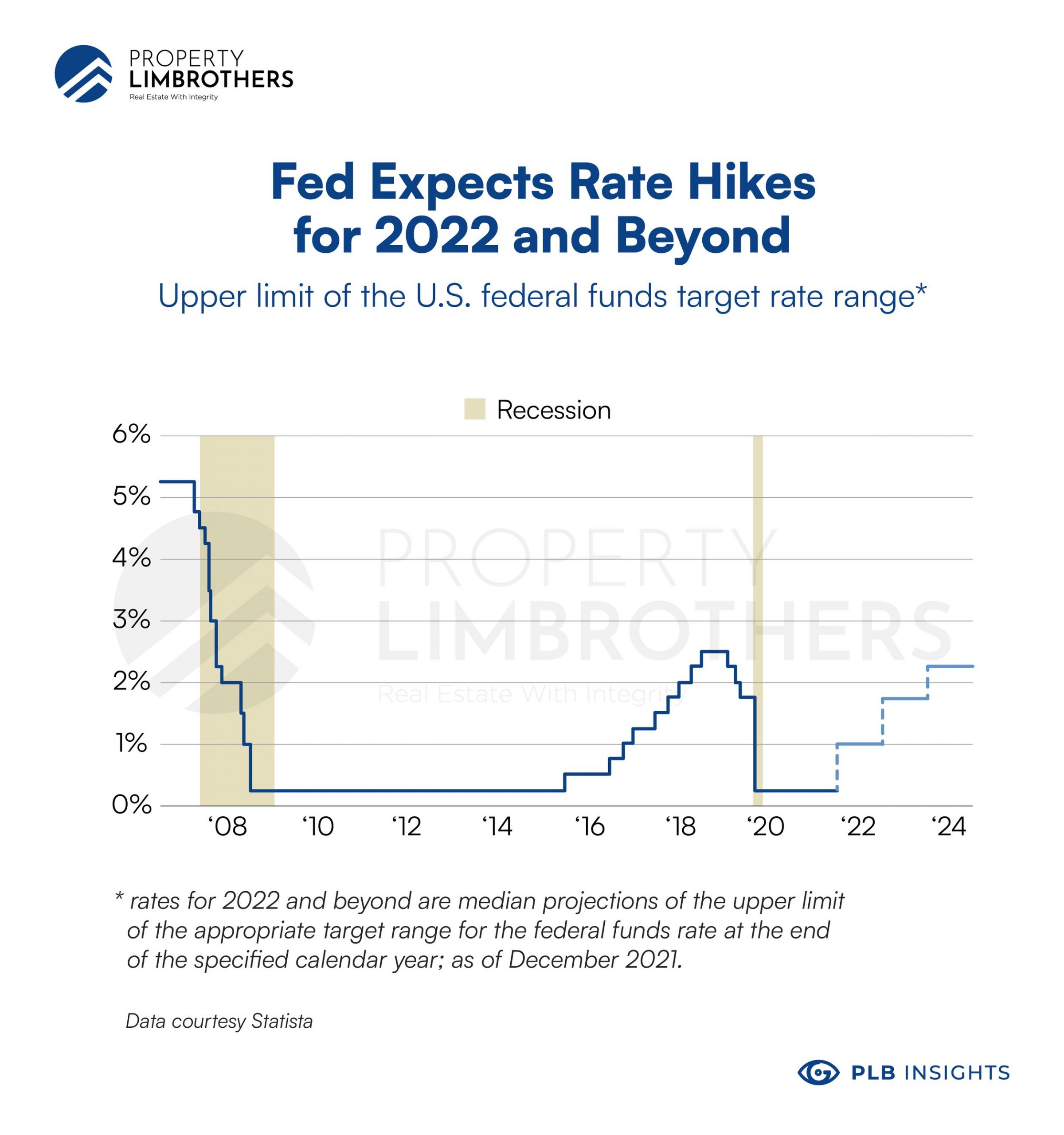
The History Of Fed Rate Changes
This isnt the first time the Fed has changed the federal funds rate. It has a history of rate increases and decreases because various events throughout time have made them necessary. Heres what the past decades have looked like in the economy and mortgage industry since data became available from Freddie Mac in 1971. The average annual mortgage rates used are for 30-year, fixed-rate mortgages.
You May Like: Is It Worth It To Refinance To 15 Year Mortgage
How Have Rate Hikes Influenced Crypto
Cryptocurrencies like bitcoin have dropped in value since the Fed began raising rates. So have many previously high-valued technology stocks. Bitcoin has plunged from a peak of about $68,000 to under $20,000.
Higher rates mean that safe assets like Treasuries have become more attractive to investors because their yields have increased. That makes risky assets like technology stocks and cryptocurrencies less attractive, in turn.
Still, bitcoin continues to suffer from problems separate from economic policy. Two major crypto firms have failed, shaking the confidence of crypto investors.
Will Another Big Hike Impact The Stock Market
Following disheartening inflation data last week, the market swooned in anticipation of a big rate hike on Wednesday. Even though inflation is cooling slightly, it’s not receding as quickly as economists had hoped. Even more alarming, core inflation data which excludes volatile food and fuel prices rose in August.
“he Fed’s rate hikes are not working, at least yet and that inflation in the real economy is getting worse, not better,” noted Brad McMillan, chief investment officer for Commonwealth Financial Network, in a research note. “Higher rates mean lower stock values.”
Stocks tumbled after the announcement, with the Dow Jones Industrial Average shedding 0.7% in Wednesday afternoon trading. In its Wednesday statement, the Federal Reserve said it “anticipates that ongoing increases” in the target range for the federal funds rate “will be appropriate,” signaling that more rate increases could be forthcoming.
You May Like: Should You Buy Mortgage Points
Fed Rate Increases Affect The Stock Marketbut Not Necessarily How Youd Think
Fed rate increases have a pretty ambiguous impact on the stock market. On the one hand, higher rates may incentivize some investors to sell stocks and take profits. But theres plenty of evidence that over the longer term, rate hikes dont hurt stocks.
In the short term, the most significant immediate impact of rate increases is on market psychology. When the FOMC raises rates, professional traders might quickly sell stocks and move into more defensive investments, without waiting for higher rates to work their way through the economy.
But over the longer term, the data shows that stock markets can rise in some cases when the Fed tightens monetary policy.
Dow Jones Market Data analyzed the five most recent rate hike cycles to see what history says about stock market returns in these periods. Their analysis showed that during these five long-term periods, the three leading stock market indexes only declined during one rate hike cycle, from June 1999 to January 2001, during the dot-com crash.
The Cost Of Owning Goes Beyond The Mortgage
Moving from renting to buying also means paying for things beyond the down payment or closing costs. Prospective buyers should also think about what kind of money theyll need after the purchase is complete, says Allen Brewington, a licensed associate real estate broker with Triplemint in New York City.
Owning a home comes with additional expenses and buyers who dont have sufficient savings are most at risk, Brewington says. When you rent, the landlord should fix everything that breaks in accordance with your lease agreement. When you own and the dishwasher breaks, youll have to fix it or purchase a new one yourself.
Renters who intend to stay in the same home for a long time should buy, rather than rent.
Brian Davis, a real estate investor and co-founder of Spark Rental
If you dont have emergency savings, Brewington says these added expenses can be more difficult to deal with. Setting up a separate savings account for home maintenance and repairs can help you prepare for the occasional financial blip that owning a home entails.
You May Like: How Much Would A Mortgage Be On 130 000
Fed Rate Hikes In 2022
In March 2022, the Fed raised its federal funds benchmark rate by 25 basis points, to the range of 0.25% to 0.50%. The rate hike marked the first time since 2018 that the Fed has increased rates.
In early May 2022, the Federal Reserve issued another statement that it would again raise the target range for the federal funds rate to between 0.75% and 1%. In an effort to lessen the size of the Federal Reserves balance sheet, the Fed also announced that it would be reducing its holdings of Treasury and mortgage-backed securities.
In June 2022, the Fed raised the rate by an additional 75 basis points, or 0.75%, in an effort to curb the continued elevation of inflation. This increase brought the target rate range between 1.5% and 1.75%, and it marked the largest single rate hike since 1994.
In July, after Consumer Price Index numbers showed inflation was 9.1% on an annual basis, the Fed raised interest rates an additional 0.75% to a target range of 2.25% 2.5%. The hope is that this takes a bite out of inflation, but it also will likely push interest rates higher for borrowers.
The Fed anticipates additional rate hikes will be necessary to hit their target inflation rate of 2%. In fact, many experts predict increases throughout 2022 with the next anticipated hike happening in September. The remaining meetings on the Fed calendar are in September, November and December.
What The Federal Reserve Does
The Federal Reserve is the nation’s central bank. It guides the economy with the twin goals of encouraging job growth while keeping inflation under control.
The FOMC pursues those goals through monetary policy: managing the supply of money and the cost of credit. Its main monetary policy tool is the federal funds rate, which is the interest rate that banks charge one another for short-term loans. Although there’s no such thing as “federal mortgage rates,” the federal funds rate influences interest rates for longer-term loans, including mortgages.
The FOMC meets eight times a year, roughly every six weeks, to tweak monetary policy. At the conclusion of each meeting, the committee releases a statement explaining its reasoning. Three weeks later, the meeting’s minutes are released, serving Fed nerds even more details.
Also Check: How Much A Month Is A 500k Mortgage
Why Is The Fed Raising Rates So Much
Inflation is extremely high. In August, prices were 8.3 percent higher than the year before. Normally, the Fed aims for 2 percent.
Even though inflation has been creeping up for more than a year, the Fed was late to intervene. For much of 2021, central bank officials insisted that inflation was a temporary feature of the covid recovery, and wouldnt become a persistent part of daily life. But over time, Fed leadersrealized they were wrong, and theyrushed to start raising rates in March.
Even once the Fed started raising rates, inflation continued to climb. The Fed has repeatedly had to ramp up its response, even at the risk of slowing the economy so much that it forces a recession.
Quick History Of The Federal Reserve
The Federal Reserve is the governments central banking authority and its agency for monetary policy. The Feds primary function is to keep the economy stable and support long-term, manageable expansion.
The Feds primary tool for managing the economy is the Fed Funds Rate, a declared interest rate for loans made between two commercial banks overnight. Overnight loans are the shortest loan terms possible. Theyre paid back to the lender each morning.
Recommended Reading: Is It Better To Pay Off Your Mortgage Or Not
How Does The Federal Reserve Affect Mortgage Rates
Apr 6, 2021 | Blog
Many people believe the Federal Reserve, through the actions of the Federal Open Market Committee, has a direct impact on mortgage rates.
Its actually more so that speeches from Federal Reserve Committee members, announcements of what the Fed is doing, and its actions in the open market serve as useful predictors of future rate movement. The Federal Reserve not only promotes maximum employment and stable prices for the American people but stabilizes the financial system.
In this article, we will discuss the structure of the Federal Reserve, how the Federal Reserve supports the economy, and how it influences the demand of the three monetary policy tools..
What is the Federal Reserves Scope?
So how does the Federal Reserve work? In this section, well give a brief overview of the function and structure of the organization.
The Federal Reserve often referred to as the Fed, is made up of 12 regional federal reserve banks that execute national monetary policy through supervision and regulation of banks in the United States. By the actions of the Federal Reserve, banking services are provided nationally and financial stability is maintained in the economy.
Monetary policy refers to three main actions undertaken by a central bank to influence the availability and cost of money and credit to help promote national economic goals. These are open market operations , or changing the discount rate and reserve requirements .
What Rate Hikes Cost You
Every 0.25 percentage-point increase in the Fed’s benchmark interest rate translates to an extra $25 a year in interest on $10,000 in debt. That means the latest 0.75 percentage-point hike will add an extra $75 of interest for every $10,000 in debt.
But that’s on top of borrowing costs that have already jumped this year.
The Fed’s five hikes so far in 2022 have increased rates by a combined 3 percentage points, or $300 in interest added on every $10,000 in debt.
Read Also: How Much Interest You Pay On A Mortgage
How Rising Fed Interest Rates Affect Home Buyers Homeowners
Many or all of the products featured here are from our partners who compensate us. This may influence which products we write about and where and how the product appears on a page. However, this does not influence our evaluations. Our opinions are our own. Here is a list ofour partnersandhere’s how we make money.
The Federal Funds Rate
The federal funds rate is the interest rate banks pay to borrow money from one another overnight. Banks with more reserves than they need can lend money to banks with less reserves than they need. This liquidity helps consumers and businesses borrow money when they need it.
The Feds current target for the federal funds rate is 1.5% to 1.75%. This rate is much higher than the 0% to 0.25% target it was aiming for in July 2021. The Fed is trying to decrease inflation to get it closer to 2% instead of the 9% the United States experienced in June 2022. By comparison, in June 2021, inflation was 5.4% already well above the Feds target.
Don’t Miss: How To Go About Getting Pre Approved For A Mortgage
What The Feds Rate Increases Mean For You
A toll on borrowers.The Federal Reserve has been raising the federal funds rate, its key interest rate, as it tries to rein in inflation. By raising the rate, which is what banks charge one another for overnight loans, the Fed sets off a ripple effect. Whether directly or indirectly, a number of borrowing costs for consumers go up.
Consumer loans.Changes in credit card rates will closely track the Feds moves, so consumers can expect to pay more on any revolving debt. Car loan rates are expected to rise, too. Private student loan borrowers should also expect to pay more.
Mortgages.Mortgage rates dont move in lock step with the federal funds rate, but track the yield on the 10-year Treasury bond, which is influenced by inflation and how investors expect the Fed to react to rising prices. Rates on 30-year fixed-rate mortgages have climbed above 6 percent for the first time since 2008, according to Freddie Mac.
Banks.An increase in the Fed benchmark rate often means banks will pay more interest on deposits. Larger banks are less likely to pay consumers more, and online banks have already started raising some of their rates.